Are you familiar with that sudden, stabbing pain in your shoulder blade that catches you off guard? It may have startled you while going through your day, leaving you wondering what's happening.
It's high time we shed some light on what could be causing this pain and how to relieve it. So let’s dive in and get rid of that pain once and for all!
What Causes Stabbing Pain In The Shoulder Blades?
There are numerous causes of stabbing pain in your shoulder blades.
The shoulder blade, also called the scapula, is a triangular bone in your upper back on both sides of your spine. It facilitates a wide range of shoulder movements, such as:
- Pushing them forward
- Pulling them backward
- Turning them around
- Raising or lowering them
Shoulder blade or scapular pain refers to discomfort in the scapula or the muscles and tissues that directly support it. However, most of the time, people associate it with shoulder pain due to the interconnected nature of these areas.
Here are some potential causes of stabbing pain in your shoulder blades:
Muscle Issues
These are the most likely causes. It can involve the muscles controlling the shoulder blade or their connecting tissues. The pain might stay only in the shoulder blade or extend to the back and shoulder.
- Muscle Strain
Shoulder blade pain can be due to strained muscles from an injury or overuse. Another common culprit is poor posture.
- Intercostal Muscle Strain
The intercostal muscles are situated between the ribs and help the rib cage expand and contract during breathing. When these muscles are strained or injured, they can lead to pain in the chest, back, and shoulder blade area.
- Rotator Cuff Injuries
These are injuries to the tendons that connect the shoulder muscles to the bones. If there is a tear present, the pain usually occurs when you raise your arms and can radiate down the rest of your arm. You may also have weakness and limited range of motion.
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome
A condition causing chronic pain affecting the muscles and connective tissues. Aside from chronic pain, you may also notice the presence of trigger points, which are tight and sensitive areas in the muscles.
- Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia causes widespread pain that may include the shoulder blades. Aside from pain, you may also notice reduced energy levels and problems with memory and concentration.
Bone and Joint Conditions
Shoulder blade pain might also stem from bone and joint problems:
- Osteoporosis
This is the weakening of bones, often in the upper back and spine. If you have osteoporosis, you may notice persistent back pain. You may also be more prone to fractures. If not treated, you might even notice a decrease in your height over time.
- Arthritis
Inflammation of the joints can also cause shoulder blade pain. You may also notice swelling in your joints, especially in your knees, knuckles, and toes. In some forms of arthritis, your joints may become deformed.
- Spinal Stenosis
Narrowing of the spinal canals can cause symptoms of a pinched nerve in the shoulder blade. You can also have back pain that radiates down your arms and legs. Other symptoms include weakness and tingling or numbing sensations.
- Costochondritis
Costochondritis is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone (sternum). This inflammation can lead to chest pain and possibly shoulder blade pain.
- Degenerative Disc Disease
Disc deterioration can lead to neck and shoulder pain. Symptoms may be similar to those of spinal stenosis, so you may notice your pain traveling down your arms and legs. You can also experience weakness and impaired sensation.
- Shoulder Blade Fractures
This is rare but can occur due to falls or accidents. You may notice tenderness and swelling in the shoulder blade area. You may also have crepitus or a popping sound when you try moving your shoulder.
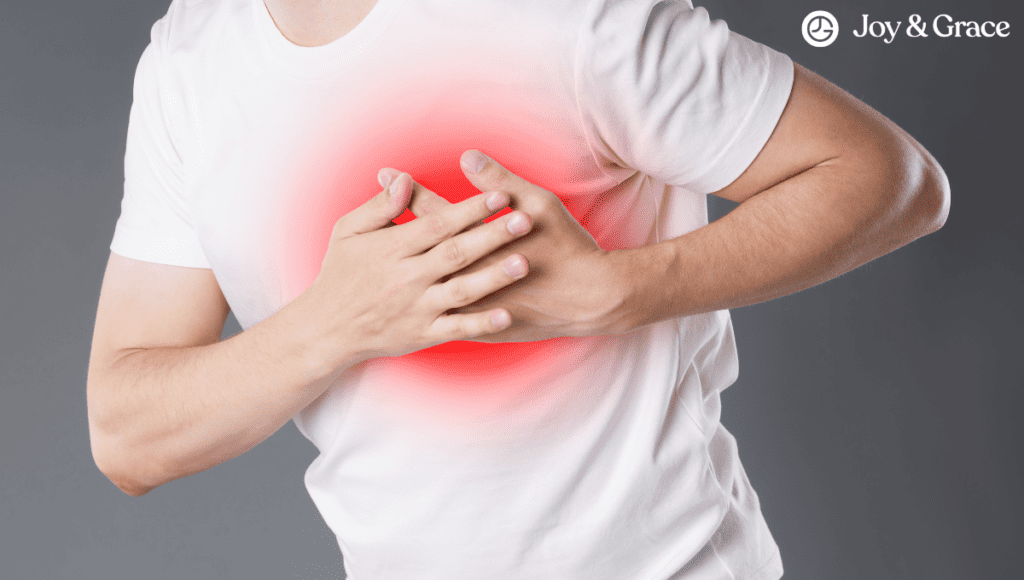
Heart Conditions
Serious heart problems might cause referred pain in the shoulder and shoulder blade:
- Heart Attack
In a heart attack (“myocardial infarction”), a portion of the heart dies due to an inadequate blood supply. The most common symptom of a heart attack is a crushing pain or discomfort in the chest that can spread to your neck, jaw, arms, and shoulder. You may also have shortness of breath, a rapid or irregular heartbeat, dizziness, etc.
- Aortic Dissection
This is a tear in the large blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the abdomen. People often describe the pain from aortic dissection as tearing or ripping. The pain can also radiate to the neck, arms, and legs. It's important to note that the symptoms of aortic dissection are dramatic. If you're experiencing mild, fleeting stabbing pain in the shoulder blades, it's unlikely to be due to an aortic dissection.
- Pericarditis
This refers to the inflammation of the lining of the heart (pericardium). The pain is usually sharp, stabbing, and worse when breathing or lying down. Other symptoms include a cough or fever.
If shoulder blade pain accompanies severe, persistent chest pain or pressure, it could indicate a heart issue.
Lung and Viral Conditions
Issues affecting the lungs, chest cavity, or chest wall can lead to shoulder blade pain:
- Pneumonia
Lung infections can inflame the lung's linings, which may also cause pain in the shoulder blade (pleurisy). Common symptoms of pneumonia include:- Fever
- Chills
- Cough with phlegm or pus
- Shortness of breath
- COVID-19
COVID-19 can also cause pleurisy. The widespread inflammation seen in COVID-19 can also cause shoulder blade pain. Symptoms can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe, and some individuals may be asymptomatic. Common symptoms include:- Fever or chills
- Dry cough
- Sore throat
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Loss of taste or smell
- Body aches
- Shingles
Shingles occur due to a viral infection. They may affect the scapular nerve, causing pain in the shoulder blade area. Symptoms typically occur on one side of the body and include:- A rash of fluid-filled blisters that eventually crust over
- Pain, burning, or tingling in a specific area
- Itching and sensitivity to touch
- Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism, or PE, is a life-threatening condition. It can happen when a piece of a blood clot in the legs breaks off and moves to the lungs.
Conditions that can increase your risk of a pulmonary embolism include:- Taking a long trip by car or plane
- Recent surgery
- Pregnancy
- Cancer
The pain is usually described as sharp and happens suddenly. Some people also have a hard time getting enough air, while others just feel a little uncomfortable. Before a pulmonary embolism happens, you might have pain, redness, and swelling in your legs, which are all signs of a blood clot.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Abdominal or pelvic conditions can also cause shoulder blade pain due to referred pain:
- Gallbladder disease
Inflammation or the presence of gallstones may also cause shoulder blade pain. Gallbladder disease often presents with:- Pain in the upper right or middle abdomen
- Pain that radiates to the back or right shoulder
- Nausea and vomiting
- In some cases, your skin may turn yellow (jaundice)
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
Sores in the digestive tract may cause referred pain in the shoulder. Common symptoms can include:- Burning stomach pain, often relieved by eating or taking antacids
- Bloating, belching, and nausea
- Vomiting blood or having dark, tarry stools in severe cases
- Acid Reflux
Similar to peptic ulcer disease, acid reflux may cause referred pain to the shoulder blade. When it becomes chronic, it's known as GERD. Common symptoms include:- Heartburn or a burning sensation in the chest
- Backflow of stomach contents into your mouth
- Cough
- A hoarse voice
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pancreatitis
An inflamed pancreas may cause pain in the right shoulder blade. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and might include:- Abdominal pain, often in the upper abdomen, that may radiate to the back
- Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite
- Swollen or tender abdomen
- Fever and rapid pulse in severe cases
Cancers
Certain cancers may spread to the scapula and cause shoulder blade pain. However, these are extremely rare cases. This can include:
- Lymphoma
- Lung Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Thyroid Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
Shoulder blade pain usually only happens when the cancer is more advanced and has spread to your bones (also called bone metastasis). Symptoms usually depend on the type of cancer, but in general, the most noticeable symptoms of metastatic cancer are:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Masses in the affected areas
Can Gas Cause Stabbing Shoulder Blade Pain?
There are no studies available directly linking intestinal gas to shoulder blade pain.
However, conditions causing excessive gas may predispose you to body aches and pains. One good example is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
According to studies, people with IBS may have hyperalgesia all over their bodies. Hyperalgesia is when your body is overly sensitive to pain. And your shoulder blades are not spared.
Another possible mechanism by which gas can cause shoulder blade pain is by irritating the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle that separates your chest cavity from your abdomen and helps you breathe.
This can be seen after laparoscopic surgeries, where excess gas from the procedure may remain in the abdomen. The remaining gas can irritate the diaphragm, leading to referred pain in the shoulder. However, this is usually reported as shoulder pain, not shoulder blade pain.
Can Stress Cause Sharp Shoulder Blade Pain?
Absolutely. Stress can indeed trigger sharp pain in your shoulder blades. When you're stressed, your body gets into fight-or-flight mode. This response triggers your muscles to tighten up, including those around your neck and shoulders. As a result, you might feel a stabbing pain in your shoulder blades.
The pain might not be known initially but may be an uncomfortable sensation that builds over time if the stressor persists.
What Does Pain In The Shoulder Blade Feel Like?
Different individuals may perceive shoulder blade stabbing pain differently. Some may describe it as:
- Dull throbbing or aching pain in the scapula. It can also feel like a sharp stab.
- Trouble lifting your arm above your shoulder
- Not being able to move your hurting shoulder as much as usual
- Hearing a snap when you move your shoulder
- Leaning to one side because of the hurting shoulder
- Seeing the shoulder blade stick out more than usual (this is also called "scapular winging")
Can A Pinched Nerve Cause Stabbing Pain In The Shoulder Blades?
Yes, it absolutely can! Think of your body as a network of roads. And nerves are like cars, using these roads to carry messages between your body and brain.
A pinched nerve occurs when something, like a bone or muscle, blocks one of these "roads" for nerves. It's like a traffic jam for your body's messages, making the affected area feel painful or uncomfortable.
Stabbing pain in your shoulder blades can come from two forms of pinched nerves:
- Cervical Radiculopathy
Cervical radiculopathy involves the compression or irritation of the nerve roots in the cervical spine (neck). Pain in the shoulder blades usually involves the C5-C8 nerve roots.
- Dorsal Scapular Nerve Entrapment or Neuropathy
This refers to a condition where the dorsal scapular nerve becomes compressed or irritated, leading to pain and poor function. This nerve originates from the cervical nerves and travels down your back. The nerve supplies certain muscles that control the movement and stability of your shoulder blades.
The dorsal scapular nerve can come from the C4-C6 nerve roots.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Pinched Nerve In The Shoulder Blade?
A pinched nerve in the shoulder blade area can cause a range of symptoms varying in intensity and duration. Remember that these symptoms can also overlap with other conditions. Common symptoms of nerve compression in the shoulder blade area include
- Pain
Sharp, shooting, or burning pain in the shoulder blade region is common. The pain might extend beyond the shoulder blade area and travel along the nearby nerve pathway, leading to discomfort in the arm, hand, or neck.
- Numbness or Tingling
You might experience a sensation of numbness or tingling in the shoulder blade, upper arm, forearm, and fingers.
- Weakness
Muscle weakness can occur in the affected arm. This can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks requiring strength or coordination.
- Limited Range of Motion
A pinched nerve can lead to stiffness and reduced flexibility in the shoulder and arm, making it challenging to move the affected area.
- Pain with Movement
Certain movements or activities might exacerbate the pain or cause it to intensify. This includes lifting, reaching, or twisting.
- Muscle Spasms
Muscles in the affected area might contract involuntarily, causing spasms that contribute to pain and discomfort.
- Sensitivity to Touch
The affected area might become more sensitive to touch, pressure, or even clothing brushing against the skin.
The location of the pain can depend on the affected nerve. According to a study, scapular pain can be felt:
- Above the shoulder blade if the C5 nerve root is affected
- Above the shoulder blade and behind your shoulder muscle (deltoid) if the C6 nerve root is affected
- In between the shoulder blades if the C7 nerve root is affected
- In between the shoulder blades and within the shoulder blades if the C8 nerve root is affected
Furthermore, the compression of the C5 or C8 nerve roots can cause superficial or deep pain. Meanwhile, compression of the C6 or C7 can only cause deep pain.
How Do I Know If Shoulder Blade Pain Is Heart-Related?
When it comes to differentiating whether it's heart-related or not, there are several signs that can guide you.
Typically, heart-related pain is not confined to one area. It usually spreads to other body parts, such as the:
- Chest
- Arms
- Back
- Neck
- Jaw
It may feel more like pressure or tightness than a stabbing sensation. Also, this type of pain often comes in waves. It could intensify with physical activity and lessen with rest.
Heart-related pain frequently comes with:
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
If you experience these symptoms along with your shoulder blade pain, it could indicate a heart issue.
While this guide can provide insights, we strongly believe there's no substitute for professional medical advice. So if your shoulder blade is giving you a lot of trouble, please don't hesitate to get it checked out for peace of mind.
How Do I Stop Stabbing Pain In My Shoulder Blade?

To stop the stabbing pain in your shoulder blade, identifying the root cause of it is crucial. If your pain persists or worsens, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. However, here are some simple tips that may help manage the pain:
- Rest
Avoid activities that strain the affected shoulder to give it time to heal.
- Ice
Apply an ice pack for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce inflammation and numb the area.
- Heat
After the first 48 hours, switch to a heating pad or warm compress to relax muscles and improve blood flow.
Are you struggling with whether to apply heat or cold for nerve pain? Check out our extensive guide on heat vs. cold!

- Over-the-counter pain relievers
Non-prescription pain medicine like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help manage discomfort.
- Posture
Maintain correct posture to avoid putting extra strain on your shoulder and neck muscles.
- Stretching
Perform gentle shoulder and neck stretches to alleviate tension and improve flexibility.
- Massage
Consider a professional massage or self-massage to help relax tight muscles.
- Gentle exercises
Gradually incorporate gentle exercises to strengthen shoulder muscles and improve range of motion.
- Ergonomic adjustments
Make sure your workspace, chair, and computer setup are ergonomically sound to prevent strain.
- Sleep position
Sleep on a comfortable, supportive mattress, and try different positions to avoid aggravating the pain.
- Avoid heavy lifting
Refrain from lifting heavy objects that could strain your shoulder.
- Hydration and nutrition
Maintain a healthy diet and stay hydrated to support your body's natural healing processes.
Remember, everyone is unique. While these tips may help lessen that stabbing shoulder blade pain, the most effective approach depends on your overall condition. A healthcare professional can provide the best advice, tailored to your needs.
How Long Does It Take For Stabbing Shoulder Blade Pain To Go Away?

Because the pain can be due to a wide range of conditions, the duration of the pain can vary significantly.
If muscle strain or overuse is the cause of the stabbing shoulder blade pain, it frequently goes away within a few days to a week. The tips we mentioned earlier can help you recover faster.
On the other hand, if the shoulder blade pain is due to a pinched nerve or rotator cuff tear, recovery might take longer. Cases of pinched nerves generally resolve in a few weeks to a few months. Meanwhile, rotator cuff tears might require physical therapy or surgery for effective healing.
If the pain is from an underlying medical condition such as heart or gallbladder disease, tackling the condition may quickly relieve your pain.
Lifestyle changes can also affect the timeline. Improving your posture and incorporating strength and flexibility exercises into your routine can reduce recovery time.
Remember, everyone's body is different, and recovery times will vary from person to person.
Always listen to your body and give it the rest it needs to heal.
What Are The Red Flags For Shoulder Blade Pain?
While not all instances of shoulder blade pain are cause for concern, certain red flags might indicate a need for medical attention. If you experience any of the following red flags along with shoulder blade pain, seek medical attention:
- Severe or sudden onset of pain
- Radiating pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Nausea or vomiting
- The shoulder blade pain is accompanied by chest pain and worsens with physical activity
- A recent injury or trauma
- Fever and other signs of infection, such as chills or cough
- Numbness or weakness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pain that persists or worsens
Takeaway
If you're grappling with stabbing shoulder blade pain, it’s essential to understand that it can come from numerous conditions. The cause can range from simple causes, such as muscle strain, to serious conditions, such as heart disease.
While simple remedies can help, they can only go so far. Getting an accurate diagnosis is important so you can receive the correct treatment and prevent any complications.