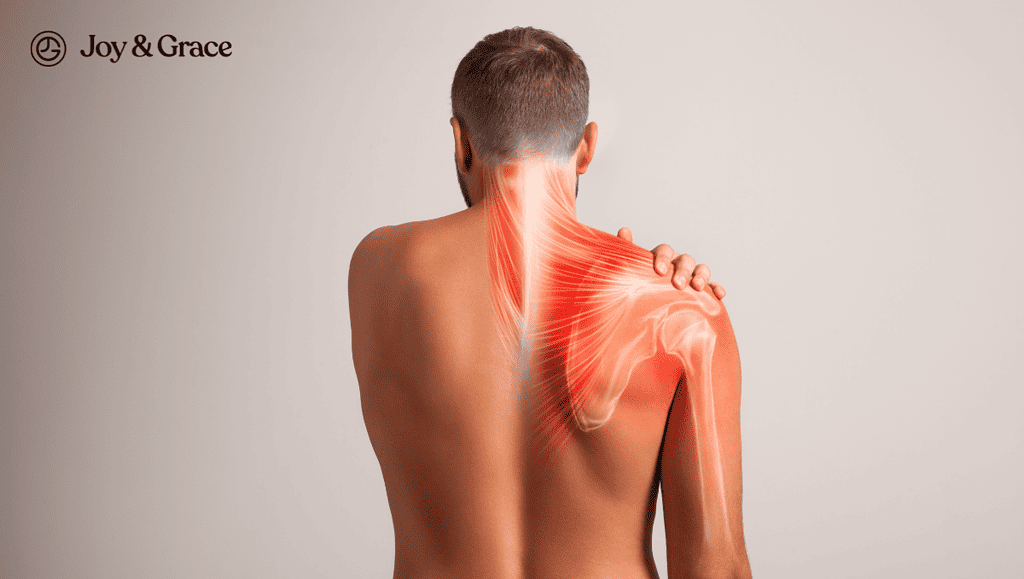
Sharp, stabbing pain in the upper left back near the shoulder blade can be alarming. While there are many possible causes, knowing the common culprits and critical symptoms can help determine if it's an ordinary strain or something more serious.
But don't let it stop you in your tracks. Join us as we dig into the possible causes and simple home remedies for taming that troublesome pain.
What Causes Sharp Stabbing Pain At The Back Of The Left Shoulder Blade?
There could be several underlying factors causing a sharp, stabbing pain at the back of your left shoulder blade. Typical culprits include:
- Pulled Muscle or Strain
Sudden, jerky movements or even just your daily routine can lead to a pulled muscle.
Activities that require you to reach up or use your arms repeatedly could lead to a pulled muscle in the shoulder blade area. Poor posture can also be a suspect.
Other common triggers could be a recent shift in your exercise routine or engaging in heavy lifting.
- Rotator Cuff Injury
Injuries to the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint, can also cause pain in the shoulder blade area.
- Acromioclavicular joint problems
Problems with your acromioclavicular (AC) joint can also lead to sharp stabbing pain at the back of your left shoulder blade. The AC joint is at the top of the shoulder, where the acromion (part of the shoulder blade) meets the clavicle (collarbone). Injuries to this joint can cause shoulder tip pain and pain radiating to nearby areas, including the shoulder blade.
- Pinched Nerve
If a nerve in your neck or upper back is compressed (such as in spinal stenosis), the pressure on the nerve can cause a sharp, shooting pain that can radiate to your left shoulder blade.
- Injury or Fracture
An injury to the shoulder or a fracture in the ribs or spine can cause sharp pain in the shoulder blade area.
- Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease common in older adults. It causes the protective cartilage cushioning the ends of your bones to wear down over time. This causes pain in any joint, including the ones in your shoulder and upper back.
While the shoulder region often takes the blame for such discomforts, it's crucial to note that not all pain originates there. Certain internal organs can produce what's known as referred pain to the shoulder blade.
Although these instances are rarer and typically manifest alongside other symptoms, it's important to be aware of them.
We'll delve into this phenomenon shortly.
Why Does My Left Back Shoulder Blade Hurt at Night?
In addition to the reasons we mentioned above, sometimes the cause of the pain could be as simple as the way you sleep. Certain sleeping positions can put extra pressure on your shoulder blade. For example, sleeping on your stomach may put you at risk for shoulder and neck pain.
Needless to say, sleeping on an injured left shoulder can also cause shoulder blade pain.
Another reason could be your sleeping environment. Check whether your mattress and pillow can adequately support your body.
What Organ Causes Left Shoulder Blade Pain?
Although most cases of left shoulder blade pain are due to musculoskeletal issues, problems with certain organs may also be the cause, as we mentioned earlier. Some organs that might trigger referred pain to the left shoulder blade area include:
Pancreas
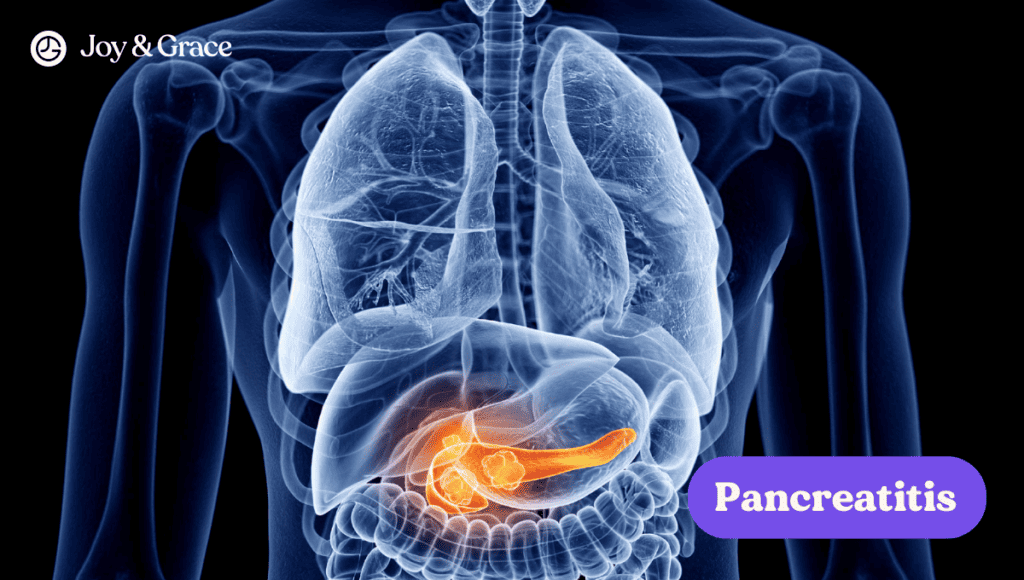
If your pancreas is inflamed, it can cause pain in your back or below your left shoulder blade. However, it’s important to note that shoulder blade pain is not the main symptom. Typical symptoms of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) include:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
Lungs
Another potential source is your lungs.
Pleuritis
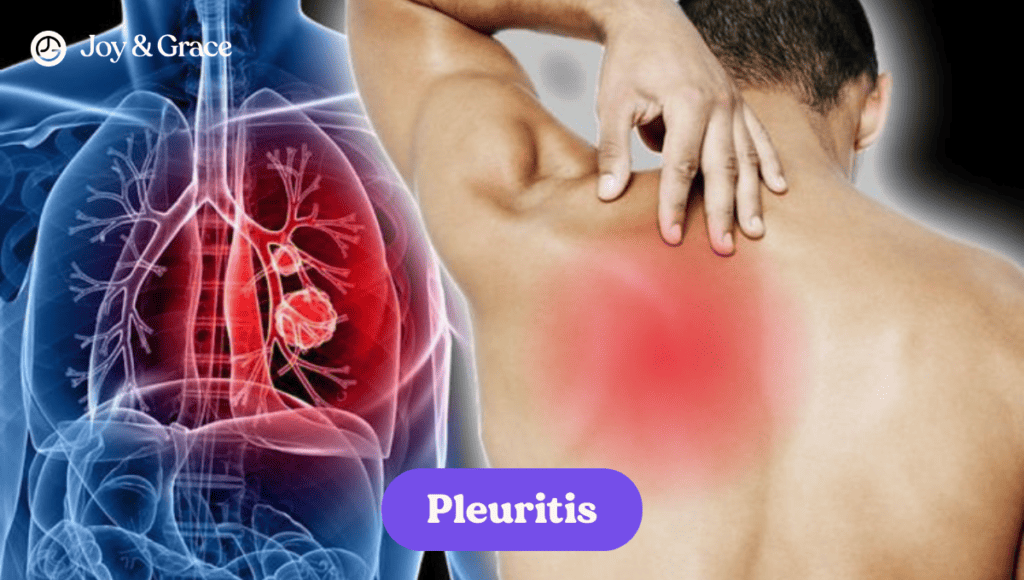
Conditions such as pleuritis, an inflammation of the membrane surrounding your lungs, can result in a sharp pain that's felt under the left shoulder blade. Infections like pneumonia can also cause left shoulder blade pain.
Typical symptoms of lung infections include:
- Cough
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
Lung Cancer
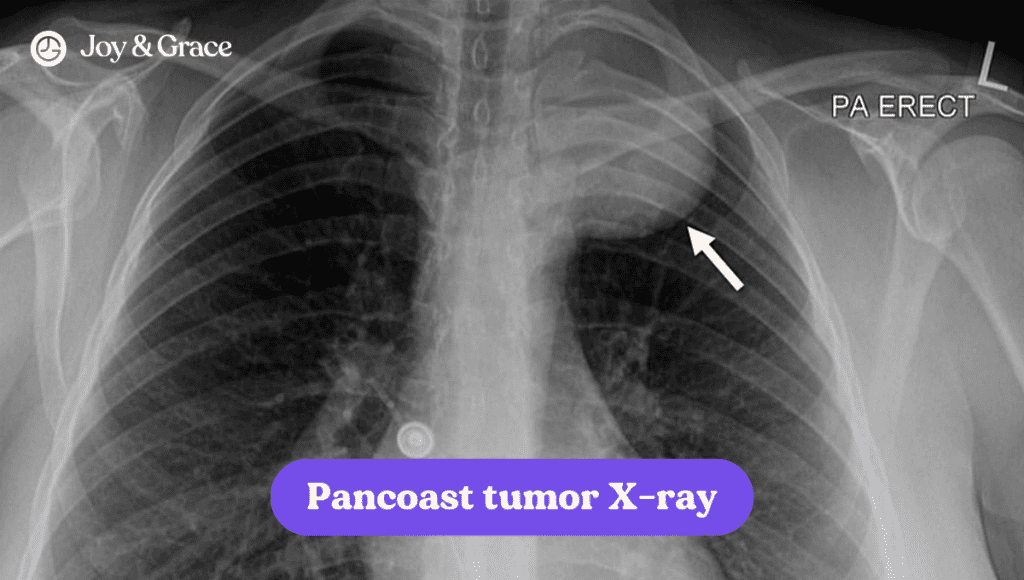
In rare cases, lung cancer can also be the culprit. Pancoast tumors, a type of lung cancer, can cause shoulder pain that can spread to your shoulder blade. It’s important to note that lung conditions can affect your left or right shoulder blades. Aside from shoulder pain, Pancoast tumors present with:
- Drooping of the upper eyelids
- Anhidrosis, or the lack of sweating
- Miosis or constricted pupils
- Weakness of the hands
- Chest pain
- Weight loss
Blood clots
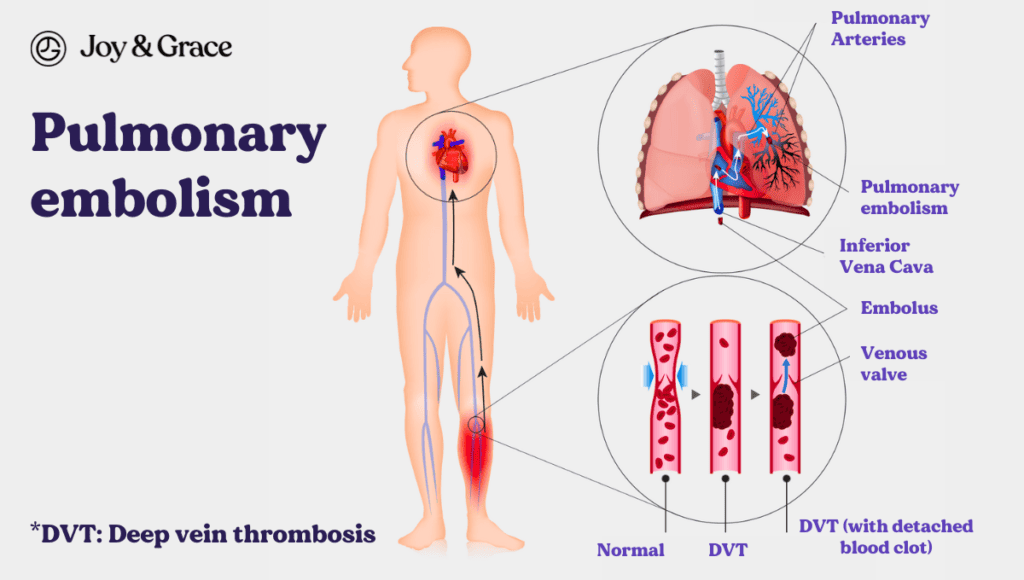
Blood clots in the lungs, medically known as pulmonary embolisms, are another important consideration. These clots can travel from other parts of the body, often from the deep veins of the legs, and lodge in the lungs. A pulmonary embolism can cause a sudden, sharp pain in the chest and back, potentially felt under the left shoulder blade.
The typical symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include:
- Sudden and unexplained shortness of breath
- Chest pain that may become worse when you breathe deeply, cough, or even eat
- Coughing up blood
- Rapid heart rate
Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. If you experience these symptoms, especially if you have known risk factors for blood clots (like prolonged immobility, recent surgery, or a history of clots), seek emergency medical care.
Stomach and esophagus
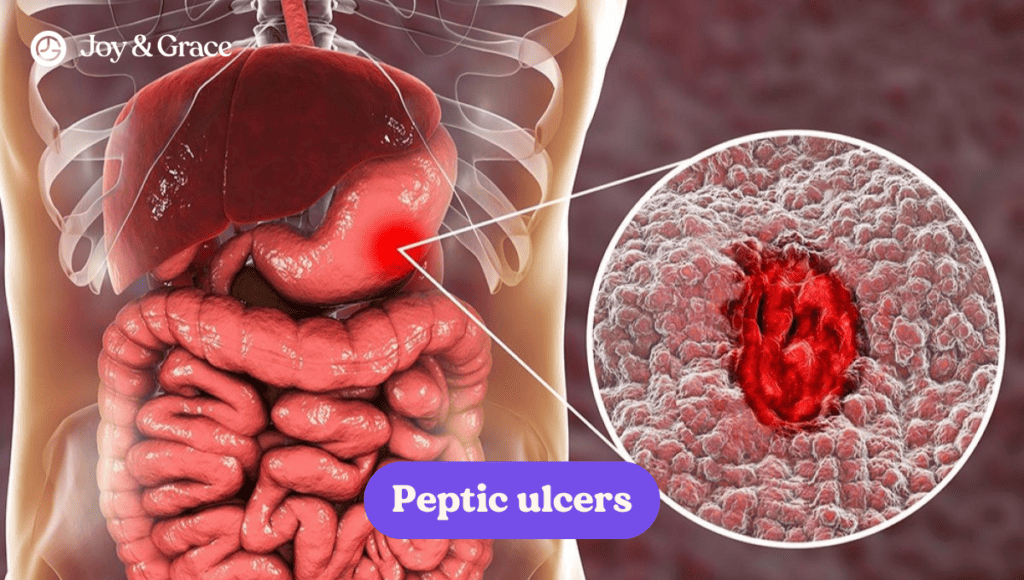
Peptic ulcers, or open sores in the lining of the stomach and intestine, can cause referred pain in the shoulder blade area. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can also cause a burning sensation and pain that may radiate to the left shoulder blade.
The main symptoms of GERD include:
- Heartburn
- Sore throat
- Hoarseness
- Regurgitation or acid backing up your throat or mouth
Heart Problems
Though shoulder blade pain isn't the most common symptom of heart issues, it does occur in some individuals.
Let's delve into this a bit more.
Can Stabbing Pain in the Left Shoulder Blade Be Heart-Related?
In certain situations, left shoulder blade pain can indeed be heart-related. A good example is angina, a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. This medical condition often presents as discomfort, tightness, or, although more rarely, stabbing pain. The pain can spread to your back, neck, jaw, shoulders, and arms, particularly your left side.
Notably, angina pain typically alleviates with rest.
A heart attack can also present as chest discomfort that may radiate to the back of your left shoulder blade. In contrast to angina, the discomfort stemming from a heart attack typically persists even at rest.
Lastly, pericarditis can also be the cause of your pain. This is the inflammation of the two thin layers of a sac-like tissue that surrounds your heart. It can cause stabbing pain in the middle of the back between shoulder blades or under them. This pain can worsen when you take deep breaths or lie flat.
While discussing heart-related issues, it’s important to briefly touch on aortic dissection, mainly for awareness. Though it's an uncommon cause for shoulder blade pain, it's a serious condition where the inner layer of the aorta, the large blood vessel branching off the heart, tears.
It can manifest as sudden, severe chest or upper back pain, often described as a tearing sensation. This condition often manifests with such severe and alarming symptoms that individuals instinctively seek immediate medical attention.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial, as aortic dissection is a medical emergency.
In conclusion, heart-related shoulder blade pain frequently coexists with other symptoms and does not primarily manifest as sole shoulder blade pain.
To better understand the distinction, it's essential to recognize specific signs that indicate a heart-related cause for your pain. Let’s explore that further.
How Do I Know if My Left Shoulder Blade Pain Is Heart-Related?

Although you can’t know for sure that your shoulder blade pain is heart-related without a proper medical evaluation, there are certain clues. Typically, symptoms like these accompany heart-related shoulder blade pain:
- Chest discomfort and/or pain
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
- Breaking out in a cold sweat
- Weakness
The characteristics of the pain can also act as clues. Pain from heart conditions often starts in the chest. As we mentioned earlier, this pain can spread to other areas and does not remain solely in the left back shoulder blade.
Another thing to consider is the timing of the pain. The pain might be related to a heart condition like angina if you notice it intensifies during physical exertion and eases when you rest.
But it’s important to note that these may also be present in other conditions. If you suspect your pain is due to problems with your heart, please seek medical advice.
What Symptoms Can I Feel With Upper Left Back Shoulder Pain?
Most of the time, the main symptom of left-back shoulder pain is just that: pain and stiffness. Your upper left back and shoulder might feel stiff, restricting range of motion. However, certain underlying causes can also introduce other localized symptoms, such as:
- Tenderness: The area could be sensitive to touch, causing pain when applying pressure. This symptom could hint at inflammation or localized injuries.
- Weakness: You might notice a lack of strength in your left arm or shoulder, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks. Difficulty using your left arm or shoulder may be due to nerve compression or muscle damage.
- Radiating Pain: The pain might spread from your upper left back or shoulder to other areas, such as your arm or neck.
As mentioned earlier, you may also have associated symptoms from other organs. This can include:
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Burning sensation in the stomach or chest
- Fever
- Cough
Remember, these symptoms can vary from person to person. If you're experiencing any of these signs, especially severe or persistent ones, speak to a medical professional. They can help determine the cause and the best way to make you feel better.
How Do I Stop Sharp Pain In My Upper Left Shoulder Blade?
If the sharp pain in your left shoulder blade is from muscle strain or other musculoskeletal causes, you can try the following:
- Give your body a break
Initially, it's essential to give your body a break and avoid further straining your shoulder.
After a period of rest, gentle movements can be beneficial. Regular, low-impact physical activity can strengthen your shoulder muscles and improve posture, thus helping to relieve and prevent further pain.
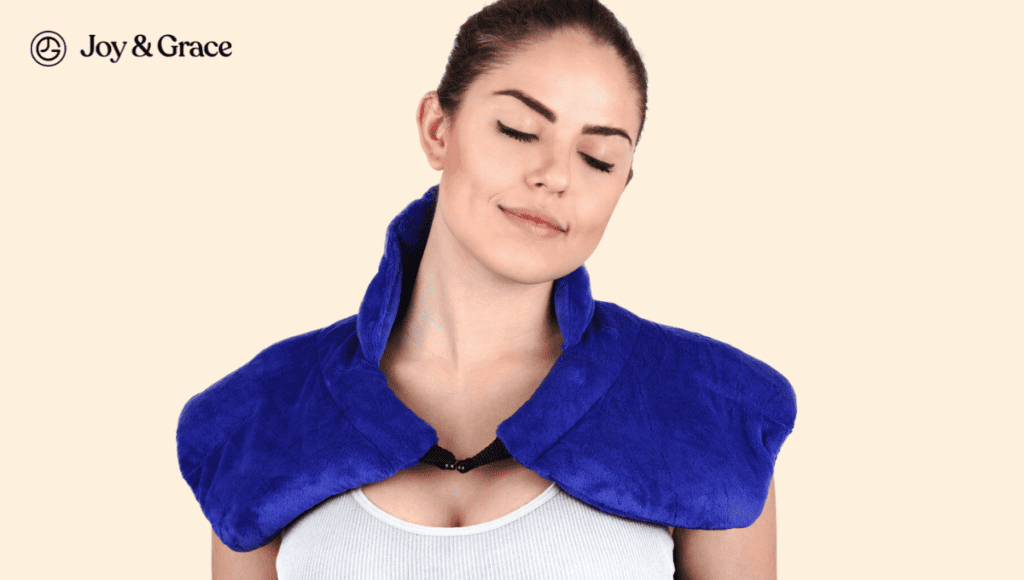
- Warm or cold compress
Apply a warm compress to your shoulder blade area to reduce muscle tension and enhance blood flow. But avoid heat if inflammation is present, which can worsen your symptoms. In these scenarios, you can try a cold compress.

- Try over-the-counter painkillers
If there's constant and severe pain present, an over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), like ibuprofen, could be helpful. NSAIDs can decrease pain and inflammation. You can also use acetaminophen (Tylenol). If you take these medications, make sure to follow the dosage instructions..
- Get moving
We know we sound like we’re contradicting ourselves, as we just told you to rest, but gentle exercises can actually help. Regular gentle exercise can strengthen your shoulder muscles and improve posture, relieving and preventing further pain.
These suggestions could offer some relief, but finding the root cause of your pain is essential. Remember that ongoing or worsening symptoms merit a conversation with a healthcare professional to develop a suitable treatment plan tailored specifically to your needs.
When Is the Stabbing Upper Left Back Shoulder Pain a Medical Emergency?
Your pain can be a one-off experience, but it can also signal a medical emergency.
If the pain behind your left shoulder blade is recurring and worsening over time, it's a glaring signal that your body is fighting an issue that requires immediate medical attention. Moreover, if your shoulder blade pain starts from the chest, it may be a medical emergency.
Aside from the other symptoms we mentioned earlier, also watch out for the following:
- Loss of appetite
- Sudden weight loss
- Coughing up blood
- Severe abdominal pain
- Changes in bowel movement
- Loss of consciousness
- Weakness in your legs
Should you or someone near you experience these symptoms, immediate medical action should be taken.
Takeaway
Left shoulder blade pain has many potential causes, like muscle strain or joint issues.
But certain red flags, like chest pain or trouble breathing, warrant an urgent doctor's visit to rule out other conditions.
Though scary, left back shoulder pain often improves with rest and conservative treatment.
Stay alert to worsening symptoms, and don't hesitate to seek medical care if concerned.