Shoulder pain, often dismissed as mere discomfort, can sometimes carry a profound message. Similarly, the heart-wrenching experience of miscarriage is a topic often shrouded in silence. It can leave lasting imprints on a woman's physical and emotional well-being.
But could these two seemingly unrelated phenomena be connected? Let's find out.
Can A Miscarriage Cause Shoulder Pain?
Shoulder pain isn't a common sign of a regular miscarriage in a normal pregnancy.
The only way a miscarriage can cause shoulder pain is:
- If the pregnancy was abnormal in the first place, or
- If there are complications during the miscarriage.
Let’s discuss these in more detail.
1. Abnormal Pregnancies
One type of abnormal pregnancy that is more commonly reported to cause shoulder pain when it miscarries is a ruptured ectopic pregnancy.
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Ectopic pregnancies are usually in the fallopian tube. This tube can rupture as the embryo grows. When that happens, it can cause bleeding inside the abdomen. If the internal bleeding is excessive, it could irritate the phrenic nerve. The phrenic nerve is connected to some nerves near the shoulder, and if irritated, it can cause the sensation of a painful shoulder.
To get into more detail: A miscarriage is when a pregnancy is lost before reaching 20 weeks gestation. Not only does it bring about emotional distress, but it can also cause physical symptoms. But, as we said at the beginning, shoulder pain isn't typically one of them.
So, what should you be on the lookout for? Well, the most common symptoms of miscarriage are vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain:
- Vaginal bleeding can range from light spotting to heavier bleeding with clots.
- Abdominal pain: Alongside the bleeding, some women may also experience abdominal discomfort. Ectopic pregnancy pain tends to be a persistent, dull, or sharp ache rather than cramping.
Other potential symptoms include:
- Vaginal discomfort,
- Nausea,
- Back pain, and
- Fatigue.
These are accompanied by the emotional rollercoaster that comes with such a loss.
Spontaneous miscarriage is a frequently encountered complication during pregnancy. It is estimated to happen in approximately 5-15% of pregnancies. Early pregnancy loss is estimated to occur in 10% of confirmed pregnancies. The majority, around 80%, take place within the first trimester.
Heterotopic Pregnancies
Did you know about this super rare and dangerous condition called heterotopic pregnancy? It's pretty wild. It's when someone has not just one but two pregnancies happening at the same time. But get this, one of the pregnancies is inside the uterus like a normal pregnancy, while the other one is actually chilling outside the uterus. Talk about a double surprise!
So, let's break it down. The pregnancy that's happening in the uterus is all good and normal. But the one outside the uterus? That's called an ectopic pregnancy (as we’ve mentioned earlier), and it usually sets up shop in the fallopian tube.
This is exactly what happened to a 33-year-old pregnant woman who arrived at the Emergency Department, per a case report published in 2019. She was feeling sharp pelvic pain and vaginal bleeding. An ultrasound confirmed a normal pregnancy. But there was no heart activity, indicating a missed miscarriage. The patient was sent home to be treated with watchful waiting (“expectant management”), but a week later, the pain and bleeding had gotten worse.
Another ultrasound revealed a mass on the right side. This was a sign of (another) ruptured ectopic pregnancy in the fallopian tubes and the retention of products of conception. The patient underwent surgery to address the heterotopic pregnancy and remove the ectopic pregnancy.
Yeah, it's pretty crazy how it can affect different parts of the body. As we explained at the beginning, the shoulder pain happens because blood from the ectopic pregnancy leaks out. The blood then irritates a nerve near the diaphragm.
2. Miscarriage Complications
Another mechanism by which a miscarriage can cause shoulder pain is when complications are present.
For example, in one reported case, a 43-year-old previously healthy Japanese woman presented with a fever and right shoulder pain. These symptoms had been ongoing for five days. Her symptoms persisted despite previous medical evaluations and treatments, including steroid injections.
Physical examination showed swelling and warmth in the right trapezius muscle. This is a muscle that inserts into the scapula (shoulder blade). The patient also had limited shoulder range of motion. X-rays showed no fractures. The MRI revealed fluid accumulation in the right trapezius with slight joint inflammation.
A fluid removal procedure yielded foul-smelling, purulent fluid. Bacteria were found in the fluid. A urine pregnancy test was also performed and came back positive.
Further examination confirmed the absence of a fetal heartbeat. This led to a diagnosis of what’s called a septic miscarriage and a muscle abscess. The abscess was located in the lower right trapezius.
You know, it's extremely rare, but this case shows that infection can spread from a miscarriage to the shoulder via the circulatory system. When a joint is infected, we call this septic arthritis. Believe it or not, it can cause some severe shoulder pain!
Septic arthritis is an infection of the joint by bacteria. It can cause severe pain in the affected joint, including the shoulder joint. Other symptoms like swelling, redness, warmth, and fever frequently accompany the pain. The joint may also be difficult to move due to the pain and inflammation.
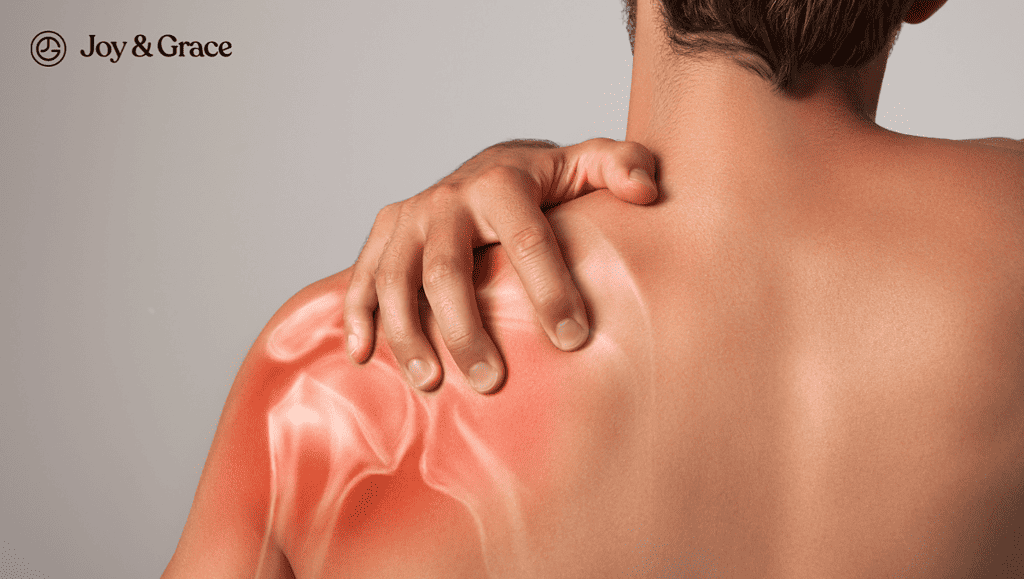
What Type of Shoulder Pain Is Associated With Miscarriage?
Shoulder tip pain is the most common type of shoulder pain associated with a miscarriage. It is an unusual pain felt where your shoulder ends and your arm begins.
The characteristics of shoulder pain related to a miscarriage can vary from person to person.
Here’s what it may feel like:
- Sharp or cramp-like pain in the tip of the shoulder
- Pain might be more noticeable when lying down
- The pain could also be described as a dull ache or stabbing sensation
- The pain may come and go or persist over time.
As we said earlier, shoulder pain typically occurs with a ruptured ectopic pregnancy and rarely with a regular pregnancy.
Why Does My Shoulder Hurt After Miscarriage?
If you have shoulder pain after a miscarriage, it is important to know that it is very unlikely that the miscarriage itself caused it.
There are other reasons for shoulder pain that you should consider. Some of these common causes include:
1. Rotator cuff tendonitis or tendinopathy:
Inflammation or irritation of the tendons of the rotator cuff. This can be caused by overuse, repetitive activities, or aging.
2. Rotator cuff tears: Partial or complete tears in the tendons of the rotator cuff, often caused by trauma or degeneration.
3. Shoulder impingement syndrome:
Compression or pinching of the tendons and bursa in the shoulder joint. It is often caused by repetitive overhead activities or poor posture.
4. Adhesive capsulitis (Frozen shoulder):
A condition characterized by stiffness and limited range of motion in the shoulder joint. It is often associated with inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule.
5. Shoulder osteoarthritis:
Degenerative wear and tear of the cartilage in the shoulder joint. This can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
6. Bursitis:
Inflammation of the bursa, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles around the shoulder joint.
7. Shoulder instability:
Dislocation or subluxation of the shoulder joint. This is often caused by loose ligaments or an injury.
8. Shoulder fractures:
Breaks or fractures in the bones of the shoulder, such as the clavicle (collarbone) or humerus (upper arm bone).
9. Tendon tears or ruptures:
Tears or ruptures in the tendons of the shoulder, such as the biceps tendon.
10. Septic Arthritis (Shoulder joint infection):
Infection of the shoulder joint, which can cause pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
When Should I Seek Medical Help If I Have Shoulder Pain After a Miscarriage?
It might be time to pay a visit to your doctor if:
1) You've been dealing with shoulder pain, and it's not showing any signs of improvement within a couple of weeks.
2) You're experiencing other symptoms.
And the important part:
If your shoulder pain comes with difficulty breathing or tightness in your chest, it's crucial to take immediate action. Don't hesitate to dial 911 or seek emergency medical help. It could be a sign of a heart attack that requires immediate medical attention. Safety first, folks!
On the other hand, if your shoulder pain is the result of an injury and you notice any of the following alongside it:
1) a joint that looks deformed.
2) an inability to use the joint or move your arm away from your body
3) intense pain or sudden swelling
It's time to ask someone to drive you to urgent care or the emergency room. These symptoms could indicate a more serious issue that needs prompt medical evaluation.
It's also a good idea to make an appointment with your doctor if your shoulder pain is accompanied by:
- Swelling,
- Redness,
- Tenderness, or
- Warmth
Remember, folks, your health and well-being are top priorities. If your shoulder pain is giving you a tough time or if you notice any worrisome symptoms, don't hesitate to seek medical attention. Your doctor is there to help you on your journey to recovery.
Where Is Miscarriage Pain Located?
Lower abdominal pain is one of the most common signs of miscarriage. Using the SOCRATES template, we can describe this pain as follows:
Site: The pain is usually located in the lower abdomen or pelvic region.
Onset: The onset of the pain can vary, but it is often sudden and may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as vaginal bleeding.
Character: Pain from an ectopic pregnancy is usually a constant, dull, or sharp ache, not cramping. It can be intermittent.
Radiation: The pain may spread to the back, thighs, or shoulder.
Associations:
Other symptoms associated with the pain may include vaginal bleeding, nausea, and fatigue.
Timing: The duration and intensity of the pain can vary and may come and go in waves.
Exacerbating/Relieving factors:
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help relieve the pain. A heating pad may also provide some relief.
Severity: The severity of the pain can vary from mild to severe.
What Do I Do If I Think I Am Having a Miscarriage?
If you're experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned in this article, it's a good idea to reach out to a healthcare professional. They'll be able to help you further by providing a thorough assessment of your condition.
When you visit a healthcare center, they will take a detailed history of your symptoms. They may perform a physical examination to gather more information. Based on their findings, they may order specific tests to aid in the diagnosis. Once they have a better understanding of your situation, they can then provide appropriate treatment or further guidance.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests that are used to evaluate early pregnancy loss include:
- Complete blood count:
A blood test that measures various components of the blood. The components are red and white blood cells, and platelets, to assess for abnormalities like anemia or infection.
- Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin levels:
A blood test that measures the levels of the hormone beta-hCG, which can provide information about the health of the pregnancy.
- Blood type and screen:
A test to determine blood type, Rh factor, and screen for any antibodies in case a blood transfusion is needed during or after a miscarriage.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy profile:
A profile of blood clotting factors, including platelet count, fibrinogen level, and prothrombin time. It is used to assess a condition called disseminated intravascular coagulopathy. It can be associated with a miscarriage.
- Urinalysis:
Analysis of a urine sample to check kidney function and detect any signs of infection or abnormalities related to a miscarriage.
Imaging studies
These studies include pelvic ultrasound scans with a vaginal probe. It may be done to rule out ectopic pregnancy and products of conception that are still in the body. It can also rule out hematometra (blood in the uterus) or other causes.
In cases where the diagnosis is unclear, other procedures can be done. These include procedures like culdocentesis or diagnostic dilation and curettage.
- Culdocentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the space behind the vagina and in front of the rectum. It is used to collect fluid or blood for diagnostic testing. It can help identify an ectopic pregnancy.
- Diagnostic dilation and curettage (D&C) involves dilating the cervix and scraping the lining of the uterus. It is used to collect tissue samples for examination. It is commonly used to diagnose and treat conditions such as abnormal uterine bleeding and miscarriage. It may also be used to remove retained products of conception after a miscarriage.
Treatment
The management of early pregnancy loss depends on the specific situation. A complete abortion usually does not require further medical treatment. There are other treatment options for a missed, incomplete, or inevitable abortion before 13 weeks of gestation (more on these later). One of them is to use a medicine called misoprostol instead of surgery.
Medicines
Pharmacotherapy (medicine) may be used in some cases. Examples are immune globulins, ergot alkaloids, antimetabolite antineoplastic agents, or prostaglandins.
Surgery
Surgical intervention may be necessary in certain situations. These are incomplete or septic abortions, ectopic pregnancies, or cases where the diagnosis is unclear. The specific surgical management procedures will depend on the individual circumstances.
Bonus: Miscarriage Classification and Mechanism of Shoulder Pain in Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
We talked about septic miscarriage as being one class of miscarriage. So, what are the other classes? Let us go through them.
Miscarriage Classification:
Miscarriage, also known as spontaneous abortion, refers to the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation. It can be classified based on various factors, including the timing of the loss, the presence or absence of symptoms, and the underlying cause. Here are some common classes of miscarriage:
1. Threatened miscarriage:
This occurs when a woman experiences vaginal bleeding during early pregnancy, but the cervix is closed and the fetus is still alive.
2. Inevitable miscarriage:
In this case, vaginal bleeding and cramping occur, and the cervix begins to dilate. The loss of pregnancy is considered imminent.
3. Incomplete miscarriage:
This refers to a situation where some of the products of conception are expelled but some remain in the uterus. The products of conception are the embryo, placenta, and gestational sac. Incomplete miscarriages often require medical or surgical intervention to fully complete the miscarriage.
4. Complete miscarriage:
This occurs when all the products of conception are completely expelled from the uterus. This eliminates the need for medical or surgical intervention.
5. Missed miscarriage:
In this type, the embryo or fetus has died, but the body has not expelled the pregnancy tissues. There may be no noticeable symptoms, and the loss is often detected during a routine ultrasound or prenatal checkup.
6. Recurrent miscarriage:
This is defined as the occurrence of three or more consecutive pregnancy losses before 20 weeks of pregnancy. It may be due to various factors. The factors include:
- Genetic abnormalities,
- Hormonal imbalances,
- Uterine abnormalities, or
- Autoimmune disorders.
7. Septic miscarriage
We mentioned this earlier. Now, let's talk in more detail about it.
A septic miscarriage is a serious complication that can happen when a woman loses a pregnancy and her uterus gets infected with bacteria. Usually, this happens when the tissue from the miscarriage doesn't completely come out of the body. It can also happen if the abortion procedure isn't done in a clean and hygienic environment.
Now, when someone experiences a septic miscarriage, they can have all sorts of symptoms. Fever, chills, abdominal pain, and a not-so-pleasant-smelling discharge are just a few of them. And if things get really bad, it can even lead to shock or organ failure.
Of course, when it comes to a septic miscarriage, immediate medical attention is crucial. Doctors will prescribe antibiotics to fight off the infection. Sometimes surgery is needed to remove the infected tissue.
So, yeah, it's definitely a scary situation, but luckily it's very rare. Still, it's good to be aware of the risk factors and seek help if anything seems off after a miscarriage. Better safe than sorry, right?
Another question that we left unanswered is:
How did a ruptured ectopic pregnancy cause shoulder pain in the case of a heterotopic pregnancy?
Mechanism Of Referred Shoulder Tip Pain
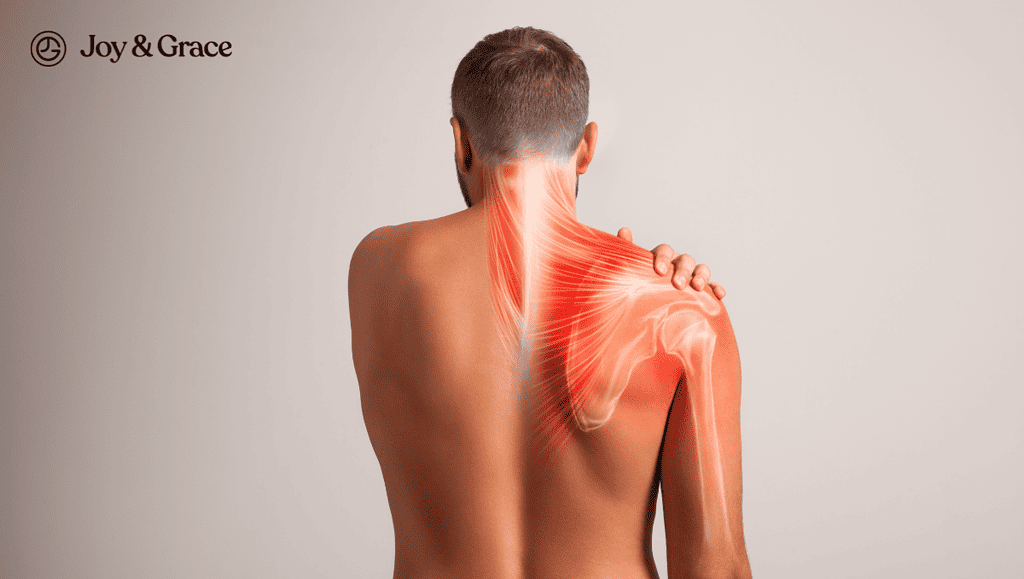
Earlier, we mentioned that the mechanism behind the referred shoulder tip pain from the diaphragm is enabled by the phrenic nerve. It involves the connection of the sensory (feeling) fibers of the nerve to the spinal cord. Stay with me. It's simple. Let me explain:
1. Phrenic Nerve Origin
The phrenic nerve originates from the C3–C5 segments of the spinal cord. It sends nerve signals to the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the main muscle responsible for breathing.
2. Sensory Fibers and Referred Pain
In addition to providing motor function, the phrenic nerve also carries sensory fibers. The fibers come from the layers located on the inferior surface.
When there is tension or irritation on the diaphragm or one of these layers, it can stimulate the phrenic nerve. This stimulation of the phrenic nerve can result in the transmission of pain signals.
3. Referred Pain and Nerve Dermatomes
The C4 segment of the spinal cord is one of the segments from which the phrenic nerve originates. It plays a role in referring pain signals to the dermatome covering the shoulder tip. Dermatomes are specific regions of the skin. They get their nerve supply from a certain spinal nerve.
In the case of the phrenic nerve, the stimulation of the C4 segment can lead to the referral of pain signals to the shoulder tip. Simple, right?
Now, coming back to ectopic pregnancy, it's necessary to emphasize this: an ectopic pregnancy is no joke. It's a serious, life-threatening medical emergency that needs immediate attention. So if anyone suspects they have one, it's crucial to get to the doctor ASAP.
Another Interesting Tidbit About Heterotopic Pregnancies
Heterotopic pregnancies are actually more common in people who use assisted reproductive technologies. An example is in vitro fertilization (IVF). They have a higher chance of multiple embryos implanting in different places. This increases the likelihood of a heterotopic pregnancy. So, it's something to keep in mind if you are going through fertility treatments.
But, heterotopic pregnancies can also happen naturally, although very rarely. The estimated rate of heterotopic pregnancy is about 1 in 100 for assisted pregnancies and 1 in 30,000 for spontaneous pregnancies.
All in all, heterotopic pregnancies are like a double whammy of surprises. They're incredibly rare, but when they happen, it's important to know the signs and get help right away.
Takeaway
In conclusion, shoulder pain is not a common symptom of a regular miscarriage in a normal and healthy pregnancy.
However, in rare cases, shoulder pain can be associated with a miscarriage if the pregnancy occurred along with an ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy outside of the uterus). This occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. If the ectopic pregnancy ruptures, it can cause heavy bleeding inside the abdomen. This may irritate the phrenic nerve connected to some nerves near the shoulder, resulting in shoulder pain.
It's important to note that other factors are more frequently responsible for shoulder pain after a miscarriage. Examples include:
- rotator cuff tendonitis and rotator cuff tears
- shoulder impingement syndrome
- adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
- shoulder osteoarthritis
- bursitis
- shoulder instability
- shoulder fractures
- tendon tears or ruptures
- or septic arthritis (shoulder joint infection)
These conditions should be considered if you experience shoulder pain after a miscarriage.
If you experience shoulder pain after a miscarriage, it is important to seek medical attention. If the pain is accompanied by difficulty breathing or tightness in the chest, it could be a sign of a heart attack. This requires immediate medical attention. It is recommended to go to an urgent medical care center or the emergency room if the pain is:
- the result of an injury
- accompanied by a deformed joint
- inability to use the joint or move the arm
- intense pain
- sudden swelling.
Remember, everyone's experience with miscarriage and associated symptoms can vary. If you have any concerns or questions, it is best to consult with health care professionals. They can provide personalized advice and guidance.