Cigarette smoking is a major health concern in the United States, causing a significant number of deaths each year. It remains the leading cause of preventable disease, disability, and death. It also results in over 480,000 deaths annually, which accounts for roughly 1 in 5 deaths. Shockingly, in 2020, almost 13 out of every 100 adults aged 18 years or older (12.5%) were current smokers.
While most people are aware of the negative effects of smoking on the lungs and heart, other parts of the body can also be affected. Recent research has linked cigarette smoking to neck pain, a common complaint that affects many people. Smokers are more likely to experience neck pain, and the severity of their pain can be worse than non-smokers.
If you enjoy a cigarette stick or two, then you might want to pay attention to this. Join us as we uncover the surprising link between smoking and neck pain.
Can Smoking Cause Neck And Shoulder Pain?
Smoking can indeed cause neck and shoulder pain.
The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause inflammation and damage to the tissues in the body. This can include the neck and shoulders' muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Smoking has also been shown to increase the risk of developing back pain and arthritis, in addition to neck and shoulder pain.
There are concrete studies that show smoking is linked to shoulder problems. This can include:
- Tears in the rotator cuff (a group of muscles and tendons in the shoulder)
- Shoulder pain
- Shoulder stiffness
Smoking may also worsen these problems and cause them to happen earlier in life.
As for neck problems, according to a study, smoking was linked to increased disease severity, higher pain scores, and progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and axial spondyloarthritis. Both of these conditions typically cause neck pain.
And without stating the obvious, smoking can also affect the way you breathe, which may also cause neck pain. In one study, smokers tend to have lesser chest expansion, making breathing harder. We talk more about the relationship between breathing and neck pain here.
Bottom line is: Smoking can lead to a variety of health problems, including musculoskeletal pain.
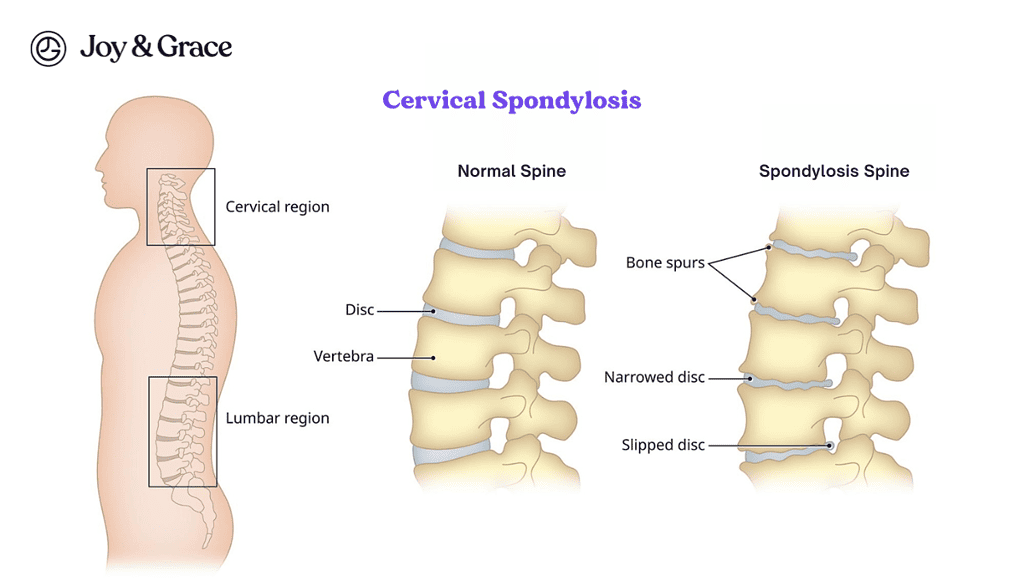
Does Smoking Cause Cervical Spondylosis?
Cervical spondylosis is a condition in which the vertebrae and discs in the neck deteriorate over time. It can lead to pain, stiffness, and other symptoms.
Studies have shown that smoking can increase the risk of developing cervical spondylosis. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause inflammation and damage to the tissues in the neck, including the vertebrae and discs. This can accelerate the degenerative process and lead to the development of cervical spondylosis at an earlier age.
Additionally, smoking can also decrease blood flow to the neck tissues and impair healing. This can further increase the chances of developing nerve damage and spinal cord compression.
In a study done in 2018, researchers randomly chose 320 patients who came to their clinic complaining of neck-shoulder pain. They divided the patients into three groups based on their smoking history:
- Active smokers
- Passive smokers
- Non-smokers.
Using the Miyazaki score, the researchers analyzed each patient's MRI films of their necks to determine the extent of wear and tear.
The Miyazaki score is a grading system doctors use to assess the severity of cervical disc degeneration based on MRI findings. It evaluates the extent of damage and loss of disc height in the cervical spine. This damage and loss of disc height can cause neck pain and other symptoms.
In simpler terms, it is a way to measure how much wear and tear there is on the discs in the neck. The grading system ranges from grade I (normal disc) to grade V (severe degeneration).
According to the study, smokers had worse Miyazaki scores than non-smokers and also reported higher pain scores. Among smokers, men had more disc damage than women, and people who smoked for longer than 10 years had worse scores than those who smoked for 5 to 10 years.
Can Smoking Cause Nerve Damage In Neck?
The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause inflammation and damage the nerves throughout the body, leading to peripheral neuropathy. This condition can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands, feet, and other body areas.
A study found that people who smoked more cigarettes had a higher chance of having neuropathic pain than people who smoked less. Neuropathic pain is a type of pain caused by nerve damage. All the following can increase the risk of developing neuropathic pain, according to the study:
- Male gender
- Diabetes
- Addiction level
- Duration of smoking
Can Smoking Cause A Pinched Nerve?

One of the most common causes of a pinched nerve is disk degeneration. And as we mentioned earlier, smoking does increase your chances of developing cervical disc degeneration. If we base it on that, then it may be likely that smoking can indirectly increase the risk of causing a pinched nerve. However, it's best to wait for studies to pop up that actually link the two. Currently, no studies suggest smoking can directly cause a pinched nerve.
Some studies suggest smoking may worsen the pain from an already existing pinched nerve, though.
Story (study) time:
A 55-year-old man became paralyzed from the waist down after being shot 22 years ago. He reported smoking about half to an entire pack of cigarettes per day. After his injury, he started experiencing burning pain in the area where he was shot, which was considered to be radicular, neuropathic pain. This pain was very intense and was rated as 7 out of 10.
Radicular pain is a type of pain that occurs when a nerve root in the spinal cord is compressed, inflamed, or damaged. Radicular pain is commonly associated with conditions such as:
- Herniated discs
- Spinal stenosis
- Degenerative disc disease.
When the man was scheduled to have surgery to fix a wound, his health care provider asked him to stop smoking. Surprisingly, his neuropathic pain disappeared immediately after he quit smoking.
He stayed smoke-free during his surgery and recovery, and his pain remained under control. When he went home, he started smoking again and found that his pain had returned. This pain was just as intense and felt similar to his pain before surgery.
What Are The Signs Of A Pinched Nerve In Your Neck?
A pinched nerve in the neck, also known as cervical radiculopathy, can cause various symptoms. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Neck pain
Pain in the neck that may worsen with movement, especially when turning the head to one side.
- Radiating pain
Pain that radiates from the neck to the shoulder, arm, or hand on one side of the body.
- Tingling or numbness
A pins-and-needles sensation or numbness that may occur in the arm or hand.
- Weakness
A feeling of weakness in the arm or hand, making it difficult to grip objects or perform everyday tasks.
Check out our article on neuropathic neck pain. It talks deeper about the other causes of neuropathic neck pain, pinched nerves, and how to relieve the pain!
Can Vaping Cause Neck And Shoulder Pain?

There are no studies directly linking vaping with degenerative disc disease. But multiple studies suggest that it can harm your bones and spine.
An experimental study done on mice showed that aerosols used in e-cigarettes can interfere with muscle repair after an injury. In mice exposed to nicotine, when their muscles were injured from overuse, the muscles could only recover about 80% of their original strength. On the other hand, muscle recovery was 100% in non-exposed mice.
This may be relevant to neck pain as the neck muscles may be affected in a similar way due to overuse or strain. The neck is supported by a complex network of muscles that work together to provide stability and mobility to both the head and neck. When these muscles are strained or overused, they can become inflamed and painful.
Does Vaping Cause Degenerative Disc Disease?

While no studies directly link vaping with degenerative disc disease, multiple studies show that vaping can harm your bones, including your spine.
There are many factors that can affect bone health, from small gene changes to exposure to polluted environments caused by vaping. Vapes contain a liquid called e-liquid, which includes toxic chemicals like cadmium and nicotine.
Some studies have shown that even low-level exposure to cadmium can negatively affect bones. Nicotine and other chemicals found in e-liquids can also damage the cells responsible for building bones. A study showed that smoking tobacco can lead to weaker bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Another study examined the effects of e-liquids and vape flavors on human bone cells. The study found that some e-liquids are highly toxic and can even reduce the cells' lifespan.
Cinnamon-flavored e-liquids were the most harmful to bone cells. Flavorless vapes, on the other hand, were the least harmful. Another study found that cinnamon-flavored e-liquids could cause oxidative stress, which can damage cells. It's important to note that these harmful effects can occur even without nicotine.
Can Quitting Smoking Cause Neck Pain?
Quitting smoking can potentially cause neck pain, although it is not a common side effect. This is because smoking cessation can lead to nicotine withdrawal, which can cause a range of psychological and physical symptoms.
What Happens If You Suddenly Stop Smoking?
If you suddenly stop smoking, your body will undergo various changes. There are both benefits and risks associated with quitting smoking abruptly. We have a great article with a section about the benefits of smoking cessation, so we’ll focus on the risks.
- Nicotine Withdrawal
Nicotine is an addictive substance, and when you suddenly stop smoking, you may experience withdrawal symptoms. Here’s a brief overview of some of the withdrawal symptoms:
- Nicotine cravings or urges are the most common symptom when quitting smoking.
- Headaches may occur as the body adjusts to the absence of nicotine.
- Nausea can also be a symptom, which may lead to vomiting in severe cases.
- Dizziness and lightheadedness are common, which can be due to changes in blood pressure and circulation.
- Feelings of anxiety, irritability, and anger may occur due to the loss of nicotine's calming effects. These effects may also go along with an increased heart rate.
- Depression and frustration may also be experienced, as smoking may have been used as a coping mechanism.
- Trouble sleeping is common, as the effects of nicotine withdrawal can disrupt sleep patterns.
- Difficulty concentrating may occur due to the lack of nicotine's stimulant effects.
- Fatigue, restlessness, and boredom may also be experienced as the body adjusts to daily activities without nicotine.
- Increased appetite may occur due to metabolic changes and increased snacking to cope with cravings.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms such as constipation, gas, or diarrhea may occur due to changes in digestion.
- Coughing, dry mouth, sore throat, and nasal drip may occur as the respiratory system begins to heal.
- Chest pain and tightness may also be experienced as the lungs begin to repair and the body adjusts to breathing without smoke.
The first 24 hours after quitting smoking or other tobacco products can be challenging, as many people experience tension and agitation. This can manifest physically as tightness in the muscles, particularly around the neck and shoulders.
- Weight Gain
Some people gain weight when they quit smoking. This is because nicotine can suppress appetite and increase metabolism. When you stop smoking, your appetite may increase, and you may be more likely to gain weight.
- Possible Relapse
Quitting smoking can be very mentally challenging. Some people may relapse without the proper support and resources to stay smoke-free.
Overall, the benefits of quitting smoking outweigh the risks. However, quitting smoking can be stressful. It is advisable to consult your healthcare provider for guidance and support to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Takeaway
In conclusion, smoking can have a devastating impact on your overall health. This includes your musculoskeletal system. Smoking can make your life miserable, from causing pain and stiffness in your neck and shoulders to damaging your nerves.
The good news is that quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk and give your body the relief it deserves. So, take the first step towards a pain-free life and throw away that cigarette. And remember to subscribe to our newsletter for more insightful articles on pain, pain relief, and wellness. Your body will thank you for it!