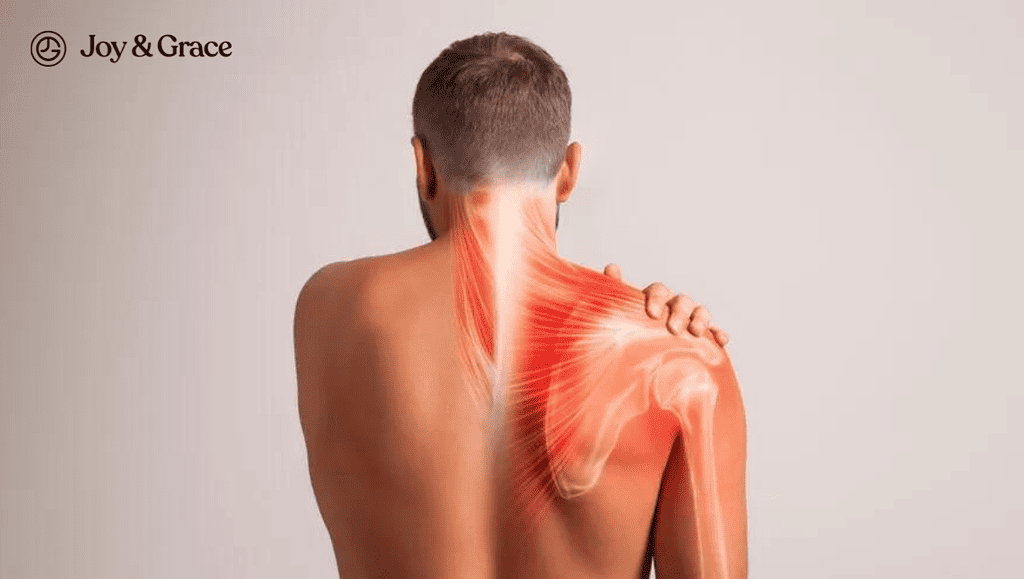
Have you been experiencing a nagging shoulder pain that just won't go away, no matter how many pain relievers you take? Have you ever considered that this seemingly harmless pain could be a warning sign of something more serious, like lung cancer?
Lung cancer is the second most common type of cancer worldwide, with an estimated 2.2 million new cases in 2020. It is a very deadly disease, so we must be aware of all its symptoms.
As we delve into the topic of shoulder pain as a symptom of lung cancer, it's important to raise awareness and shed light on the connection between the two. So, buckle up, and let's explore this important topic together.
Can Lung Cancer Cause Pain In The Shoulder Blade?
Although shoulder blade pain is not a common symptom of lung cancer, it does occur in certain types of lung cancer. It can also happen if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). These types are distinguished by the appearance of the cancer cells under a microscope and how they behave.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for about 80-85% of cases. There are several subtypes of NSCLC, including:
- Adenocarcinoma: This is the most common subtype of NSCLC, and it typically starts in the cells that line the air sacs of the lungs.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: This subtype of NSCLC typically starts in the cells lining the lungs' airways.
- Large cell carcinoma: This is a less common subtype of NSCLC, and it can start in any part of the lung.
- Pancoast tumors: These are a type of lung cancer that start in the upper part of the lung, near the neck. Pancoast tumors are a type of NSCLC, typically adenocarcinoma.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a less common but more aggressive form of lung cancer. It typically grows and spreads more quickly than NSCLC. SCLC is often associated with smoking and is rarely found in people who have never smoked.
Another type of lung cancer is mesothelioma. This is a rare type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, called the pleura, or the lining of the abdomen called the peritoneum. Mesothelioma is most commonly associated with asbestos exposure. It can take several decades to develop after exposure to asbestos.
Lung tumors can also result from other cancers spreading to the lungs. The two types of lung cancer usually associated with shoulder pain are Pancoast tumors and Mesotheliomas. However, it's not exclusive to these types.
How Does Lung Cancer Cause Shoulder Pain?
Lung cancer can cause shoulder pain in different ways. This can depend on the type of lung cancer and the stage of cancer. We've outlined these below:
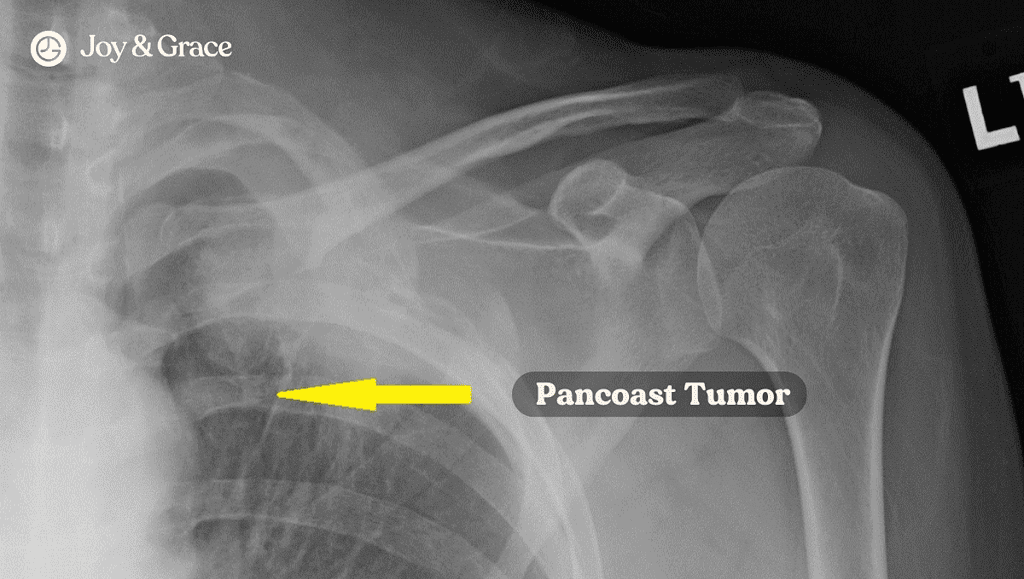
Pancoast Tumor
Pancoast tumor, also known as a superior sulcus tumor, is a type of lung cancer located at the very top of the lung near the shoulder blade. Due to the tumor's location, it is close to the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that controls movement and sensation in the arm.
If the tumor invades the brachial plexus and other nearby nerves, it can cause a group of symptoms called Pancoast Syndrome. This includes the following:
- Pain in the shoulder and arm on the same side of the body as the tumor.
- A tingling or burning sensation in the arm, hand, or fingers.
- Weakness in the arm, hand, or fingers.
- A wasting away of the muscles in the palm near the thumb.
- Horner's syndrome - A group of symptoms that include:
- Drooping of the eyelid (ptosis)
- Constricted pupil (miosis)
- Decreased sweating (anhidrosis)
Shoulder pain is usually the only symptom in the early stages of a Pancoast tumor. This usually radiates down the arm, following the path of your ulnar nerve.
In a case of a Pancoast tumor in a 71-year-old woman, the initial complaint was shoulder and chest pain. The patient also complained of reduced sensation and weakness in her arm.
In another case, a 58-year-old man complained of worsening shoulder pain that radiated down his right arm and finger. This was accompanied by weakness of the right arm and swelling of the right hand.
Mesothelioma
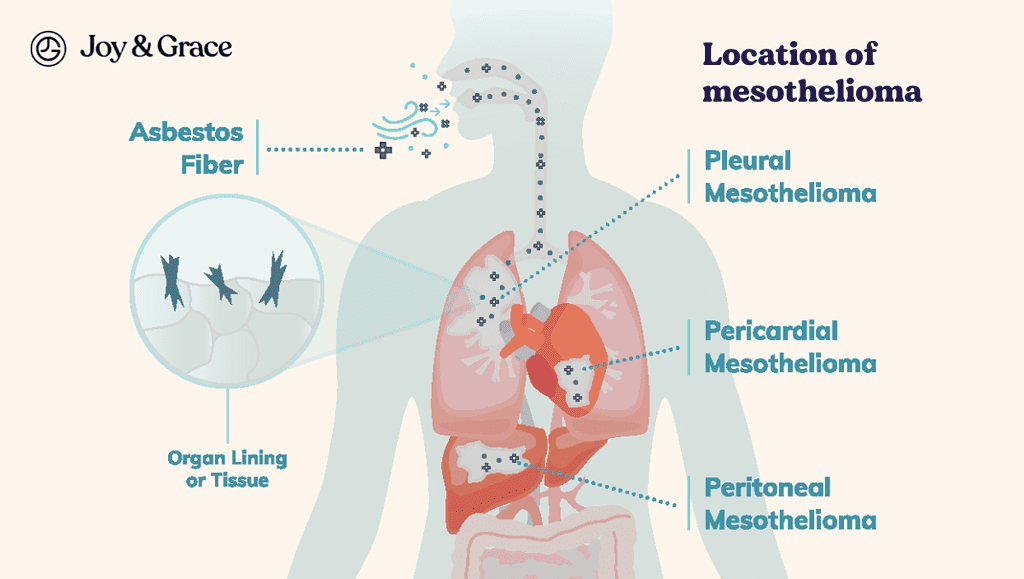
Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer affecting the mesothelium, a thin layer of tissue covering the body's internal organs. It is most commonly found in the pleura (the lining around the lungs). But, it can also develop in the peritoneum (the lining around the abdomen) and the pericardium (the lining around the heart).
Mesothelioma is mostly caused by exposure to asbestos. Asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral that was widely used in construction and other industries in the past. When asbestos fibers are inhaled or ingested, they can become trapped in the mesothelium. This can cause damage over time and lead to the development of mesothelioma.
In one study, 14.3% of patients had shoulder pain as the initial symptom of malignant mesothelioma. These patients rated the shoulder pain a 4/10. According to the study, the shoulder pain may be due to the cancer affecting the nerves of the chest wall. These irritated nerves end up sending pain signals to the shoulder, neck, and shoulder blades.
In a case of malignant pleural mesothelioma in a 22-year-old woman, her only complaint was a pain in her right shoulder blade.
Mesothelioma may also present similarly to arthritis. In a case of mesothelioma in a 67-year-old man, he had pain in his shoulder and finger joints.
Metastasis
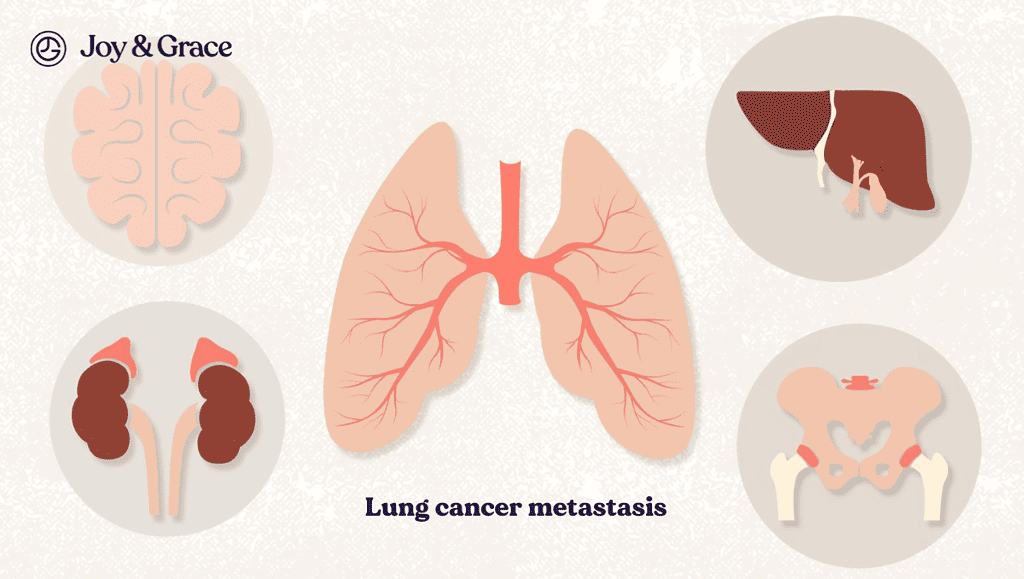
Lung cancer can cause shoulder pain if the cancer cells have spread (metastasized) to the bones, including the shoulder blade. This is known as bone metastasis.
When lung cancer cells spread to the bones, they can cause damage and destruction to the affected bone, leading to pain and tenderness. In some cases, the cancer cells can also interfere with the normal function of the bone. This can cause it to weaken and become more susceptible to fractures.
The cancer can also spread to the muscles. However, it's quite an uncommon occurrence. When it does happen, it can cause pain, weakness, and loss of function in the affected muscles.
In one case, a 47-year-old man suffered from severe shoulder pain. Medical imaging showed lung cancer metastasis to two rotator cuff muscles.
In another case, a 76-year-old woman presented to the emergency room with pain in her left shoulder, which radiated to her elbow. Medical imaging revealed that she also had fractured ribs despite having no recent accidents or trauma. This was accompanied by swelling in her legs and fluid in her lungs. She was later diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma.
Shoulder pain may also result from metastasis to distant organs, producing referred pain. In one case, a 60-year-old man developed pain in his shoulders after achieving partial remission from small-cell lung carcinoma. Upon imaging, it was discovered that the cancer had spread to his adrenal glands. This caused excitation of the diaphragm, which resulted in the referred pain.
What Are Other Signs That Lung Cancer Has Spread?
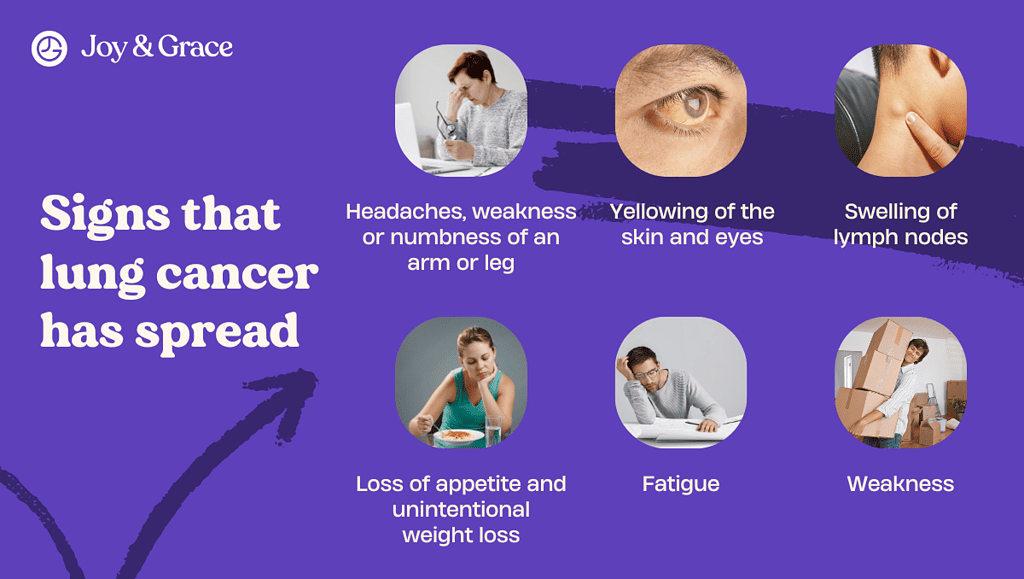
When lung cancer spreads (metastasizes) to other body parts, the signs and symptoms will depend on which part of the body is affected. Common areas for lung cancer to spread include the brain, bones, liver, and adrenal glands.
Some common signs and symptoms of metastatic lung cancer may include the following:
- Headaches, weakness or numbness of an arm or leg, dizziness, balance problems, or seizures (if the cancer has spread to the brain)
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice) (if the cancer has spread to the liver)
- Swelling of lymph nodes
- Loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue
- Weakness
What Kind Of Shoulder Pain Does Lung Cancer Cause?
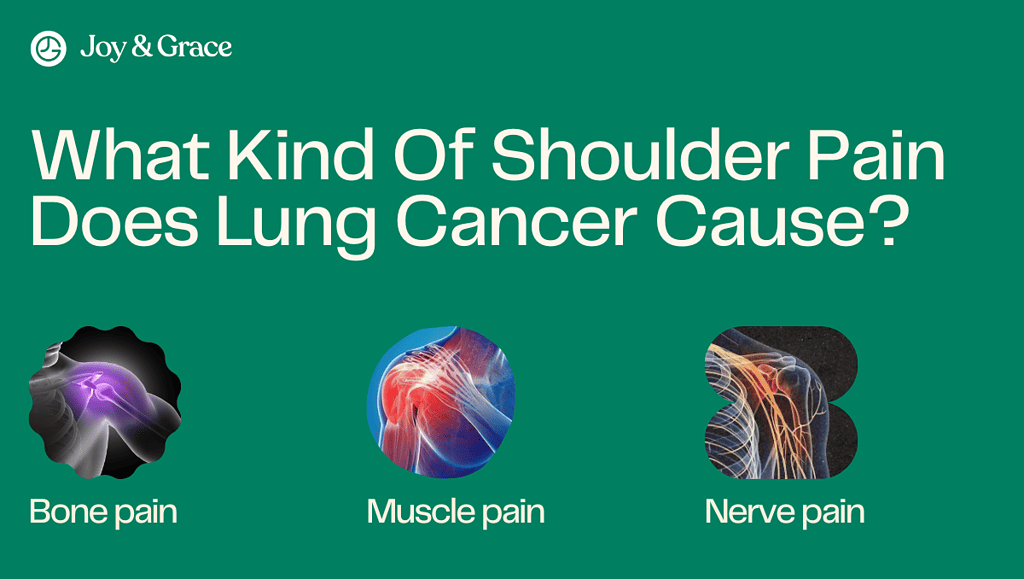
As we mentioned earlier, it will depend on the type of lung cancer and whether it has spread to other organs. The shoulder pain from lung cancer may be:
- Bone pain
- Muscle pain
- Nerve pain
What Does Shoulder Pain From Lung Cancer Feel Like?
When lung cancer spreads to the bones of the shoulder, it can cause a deep, aching pain. In some cases, the cancer may also weaken the bones, leading to a fracture. Bone metastasis can occur in 30-40% of lung cancer patien.
When lung cancer spreads to the shoulder muscles, it can cause diffuse, tender pain. This may be accompanied by muscle weakness, fatigue, and tenderness. In severe cases, the pain may also interfere with the shoulder's normal movement and range of motion. Metastasis to the muscles is considered rare and typically presents with pain and a lump or mass.
Nerve shoulder pain caused by lung cancer typically feels like a dull or sharp ache that may be constant or intermittent. The pain can also be described as burning, tingling, or electrical sensations. Sometimes the pain may radiate to your neck, back, or down your arm.
The severity of the pain can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the individual's pain tolerance.
Sometimes, the pain may be exacerbated by certain activities, such as deep breathing or coughing.
Where Is Shoulder Pain Felt With Lung Cancer?
No area is exclusive to shoulder pain associated with lung cancer. Most cases of shoulder pain associated with lung cancer report pain in the upper part of the shoulder, near the collarbone, or shoulder joint. Rarely, pain may also be felt in the shoulder blade.
Is Shoulder Pain From Lung Cancer Constant?
The frequency and duration of shoulder pain from lung cancer can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience constant pain, while others may only feel pain when they move the affected arm or engage in certain activities. The pain can also be intermittent, coming and going at irregular intervals.>>>
What Does Lung Cancer Feel Like When It Starts?
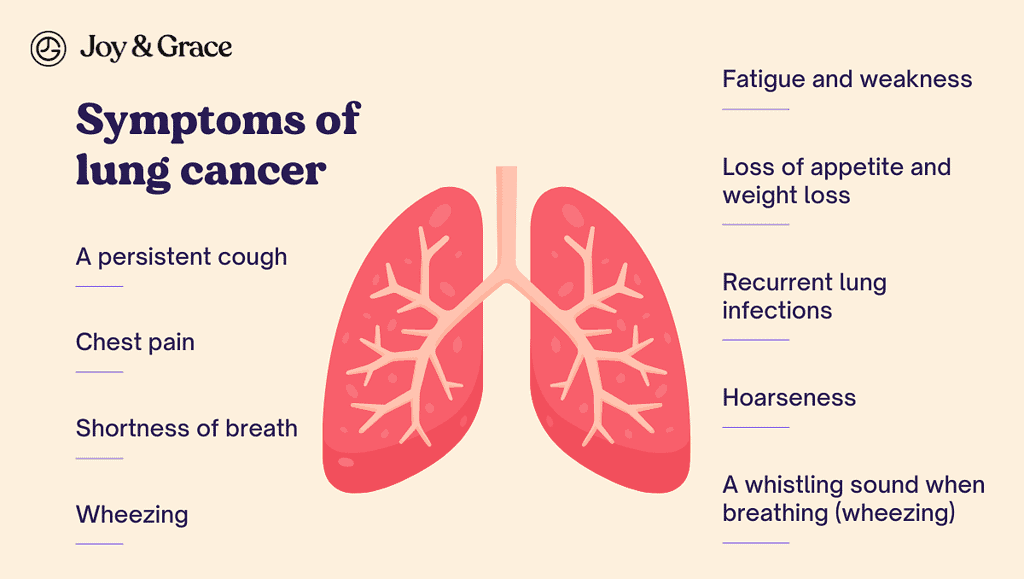
In its early stages, lung cancer may not cause any noticeable symptoms. As the tumor grows, some common symptoms can develop, including:
- A persistent cough that may be accompanied by coughing up blood
- Chest pain, especially when deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Recurrent lung infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis
- Hoarseness
- A whistling sound when breathing (wheezing)
In a 2020 study, cough (46.6%) was the most common symptom, followed by shortness of breath (33.9%). However, the absence of these symptoms and pain does not rule out lung cancer. In the same study, 27.7% of patients with stage IV lung cancer had no symptoms.
What Is Lung Cancer Cough Like?
A cough associated with lung cancer can be persistent and may not go away with over-the-counter remedies. Some common characteristics of a lung cancer cough include:
- A persistent cough that lasts for more than 8 weeks
- A cough that gets worse over time
- The cough may initially be dry but will eventually produce phlegm or mucus. Sometimes you may have "hemoptysis," which means you are coughing up blood.
- Chest pain or discomfort, especially when coughing
According to one study, up to 57% of people with lung cancer will have a cough. This percentage increases as the disease progresses.
It's important to note that other conditions, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, can also cause these symptoms. That's why it's essential to see a doctor if you're experiencing a persistent cough, especially if it's accompanied by any of the other symptoms we listed earlier.
What Should I Do If I Suspect My Shoulder Pain Is From Lung Cancer?
If you suspect that your shoulder pain might be related to lung cancer, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. A doctor or healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms and determine the underlying cause of the pain. They may also perform tests, such as imaging scans, to help diagnose the problem.
Can I Still Have Shoulder Pain After Lung Cancer Treatment?
Yes, it is possible to have shoulder pain after lung cancer treatment. There are several potential causes of shoulder pain after lung cancer treatment, including:
- Surgery
Lung cancer may be treated by surgery. There are different types of lung surgery depending on the extent and location of the lung disease or condition. Here are some of the common types of lung surgery:
- Lobectomy: This is the most common type of lung surgery and involves the removal of a lobe of the lung. The lungs are divided into lobes, each with a bronchial tube. A lobectomy is usually done to remove lung cancer or treat severe lung infections like tuberculosis.
- Pneumonectomy: This surgery involves the removal of an entire lung. Pneumonectomy is usually done when a person has a large lung cancer that involves the entire lung. It may also be done when a person has severe lung damage from emphysema.
- Segmentectomy or wedge resection: These surgeries involve the removal of a small part of the lung. Segmentectomy is the removal of a segment of the lung, while a wedge resection is the removal of a small, wedge-shaped piece of the lung. These surgeries may be performed when a person has a small lung cancer or a lung nodule.
- Lobectomy: This is the most common type of lung surgery and involves the removal of a lobe of the lung. The lungs are divided into lobes, each with a bronchial tube. A lobectomy is usually done to remove lung cancer or treat severe lung infections like tuberculosis.
In one study, 40.5% of patients who underwent lung resection developed shoulder pain. According to the study, this may be due to the duration of the operation and post-op stiffness. The pain typically resolves within 4 days.
Shoulder pain from lung surgery may be due to injury to the following:
- Shoulder structure
- brachial plexus
- phrenic nerve
- diaphragm and other surrounding structures.
- Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a common lung cancer treatment but can also cause shoulder pain. This is because radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells, which can also damage healthy cells.
When the radiation field includes the shoulder area, it can cause pain and inflammation in the shoulder. This may be persistent or temporary.
In one case, a 70-year-old man developed severe pain in his right shoulder 5 months after receiving radiotherapy for lung cancer. Imaging showed that there was inflammation in his shoulder and chest muscles. The swelling from inflammation resulted in the compression of the nerves of his brachial plexus. He was diagnosed with radiation-induced myositis.
- Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can cause a condition called chemo-induced peripheral neuropathy. This condition can result in pain, numbness, or tingling in the arms, hands, legs, or feet, including the shoulder. This is because chemotherapy drugs can damage the nerves that control movement and sensation.
Takeaway
Shoulder pain can be a symptom of lung cancer, but it is important to note that not all cases of shoulder pain are related to lung cancer. Numerous other conditions can cause similar symptoms. If you suspect that your shoulder pain may be caused by lung cancer, it is essential to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Early detection and treatment of lung cancer can significantly improve the chances of a successful outcome. So if you are experiencing persistent shoulder pain, do not hesitate to seek medical attention.