While shoulder pain is something most of us are acquainted with, nerve pain in between your shoulder blades may be something new to you. Like shoulder pain, it can be caused by various factors and may be mistaken for other conditions.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for nerve pain in
By the end of this article, we hope to provide you with valuable information that will help you manage your nerve pain and improve your quality of life.
What Does Nerve Pain in Both Shoulder Blades Mean?
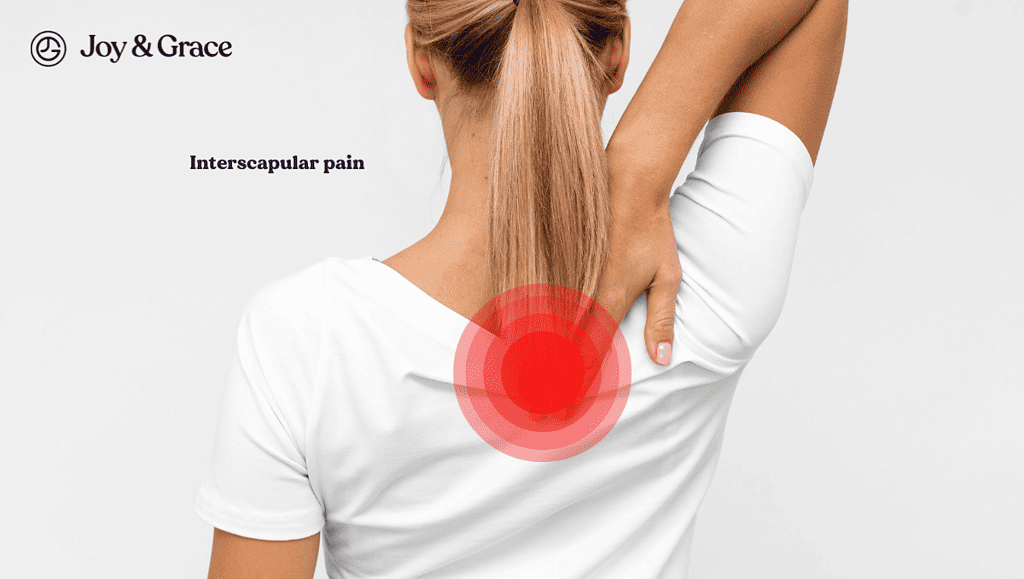
Pain between your shoulder blades or scapulas is called “interscapular pain.” It could be caused by various conditions. However, one of the most common causes of nerve pain between your shoulder blades is compressed or irritated nerves. This is termed a “pinched nerve” or radiculopathy.
This can happen when the nerves that run from your neck (cervical spine) and upper back (thoracic spine) pass through tight spaces. These tight spaces can be caused by tense muscles or changes in the structure of your spine. When your nerves get squeezed in these tight spaces, they get inflamed, which can result in pain.
This may also be accompanied by what’s called scapular winging. Scapular winging is a condition where the shoulder blade might stick out or even look like it's "winging" off the back.
If you want more detail: A nerve that may cause interscapular pain when irritated is your dorsal scapular nerve. When this occurs, it can lead to a condition called dorsal scapular nerve neuropathy. This nerve can originate from your C4-C5 and possibly the C6 nerves. So any condition affecting these nerves may also cause pain between your shoulder blades.
What Type of Disorders Can Cause Nerve Pain in the Back Between the Shoulder Blades?
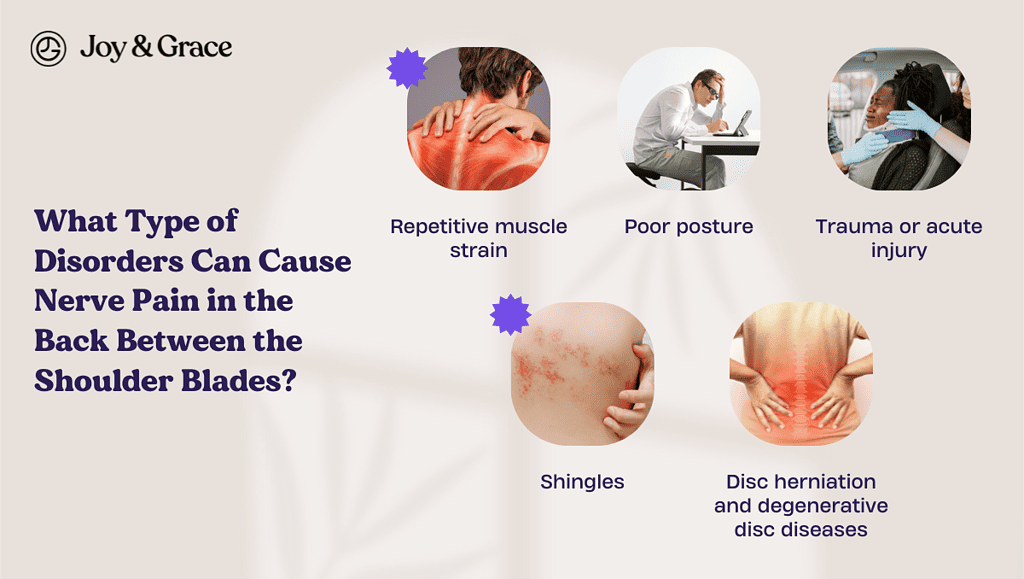
Many conditions can cause nerve pain between your shoulder blades. These include:
- Repetitive muscle strain
Activities that involve repetitive motions can cause the muscles to become tight and compress the nerves. This can include activities such as carrying a heavy backpack, for example. In one case, a man whose work involved carrying heavy bags daily suffered from scapular pain and winging.
Another case reported siblings exhibiting signs of dorsal scapular nerve neuropathy. This was attributed to recurrent overhead movements due to playing volleyball.
- Poor posture
Slouching or hunching over a desk for extended periods of time can cause the muscles and tissues in the upper back to become tight and compress the nerves. These tight muscles and tissues may then compress the nerves.
This was the case for an 18-year-old female patient who suffered from right scapular pain and winging for a year. An examination showed her shoulder muscles were not working properly due to dorsal scapular nerve neuropathy.
The researchers believe this was caused by her 30-month-long habit of studying four to five hours daily. They suggested that prolonged stretching of the dorsal scapular nerve due to bad posture may lead to chronic neuropathy.
- Trauma or acute injury
A sudden impact, such as a fall or car accident, can cause damage to the nerves in the upper back and lead to a pinched nerve.
In one reported case, a woman suffered back and shoulder pain and scapular winging four years after a car crash. She was later diagnosed with dorsal scapular nerve compression.
- Shingles
Shingles can cause nerve pain between your shoulder blades. Shingles typically causes a painful rash that can occur anywhere on the body. The rash is often accompanied by other symptoms, such as burning, tingling, or shooting pain in the affected area.
If the rash occurs between your shoulder blades, the pain can radiate to the surrounding spinal nerves and cause nerve pain. This can be a common symptom of shingles and may last even after the rash has disappeared.
If you want to learn more about shingles, we have an article here.
- Disc herniation and degenerative disc diseases
Discs are the cushions between the vertebrae in your spine. When a disc herniates (part of the inside of the disc bulges out), it can put pressure on nearby nerves, leading to pain and discomfort.
Conditions like osteoarthritis can also affect the nerves by causing the bones and cartilage of your spine to degenerate. If left untreated, "bone spurs" might form, which may then eventually compress the nerves. When this happens, it’s called “spinal stenosis.”
Can Spinal Stenosis Cause Pain Between Shoulder Blades?
Yes, spinal stenosis may cause referred pain between your shoulder blades. A study shows this is more common when it affects the C4-C7 vertebra.
Spinal stenosis can also cause a type of intense burning sensation in your shoulder blades. This medical condition is called notalgia paresthetica. In one case report, a 37-year-old woman suffered from the condition due to cervical disk disease and stenosis at her C4-C7 vertebra.
Can Multiple Sclerosis Cause Shoulder Blade Pain?
Multiple sclerosis can present with all sorts of symptoms (that’s why it’s called the great imitator). However, no distinct studies are available on whether multiple sclerosis can cause pain between your shoulder blades.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. In MS, the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers called myelin. This leads to inflammation and damage to the nerves.
In a way, MS can be thought of as a "short circuit" in the nervous system. The signals that are supposed to travel smoothly through the nerves are interrupted or blocked. This can result in pain and discomfort in various body parts, which may include the region between your shoulder blades.
According to a study, upper back pain is more common in the early stages of the disease. In the same study, upper back and shoulder pain were more common in women.
What Does a Pinched Nerve Feel Like Between Shoulder Blades?
A pinched nerve in between your shoulder pain can feel like:
- A dull ache or tightness
- Burning or shooting and sharp pain
- Pain that spreads to your arms and neck
- Limited shoulder movement
- Numbness or tingling sensations
How Do You Release A Pinched Nerve In Your Shoulder?

Pinched nerves in the shoulder can be very uncomfortable and even debilitating. The good news is that there are several methods you can use to release a pinched nerve in your shoulder.
Here are some simple tips to get you started:
1. Stretch your shoulder
However, if the pinched nerve is caused by something more serious, like a herniated disc, these measures may not be enough to relieve the problem. In some cases, they can even make the pinched nerve worse. So always consult with a healthcare professional first!
2. Massage
Massaging the area around the pinched nerve can help to release tension and alleviate pain. Start by applying gentle pressure to the area around the shoulder blade and working your way outward.
Heat or cold therapy can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. They may also help relieve muscle tension, which may be pressing on your nerves. So, if you’re looking for a relaxing way to help release a pinched nerve, try out our very own heating pad!
4. Change your posture
Poor posture can exacerbate pinched nerves in the shoulder. Be mindful of your posture throughout the day, and make sure to sit with your shoulders back and your head aligned with your spine.
5. Adjust your sleeping position
If you tend to sleep on your side, try placing a pillow between your arms to keep your shoulders level. This can help alleviate pressure on the pinched nerve.
6. Consult a healthcare professional
If your pinched nerve is severe, consult a healthcare professional. Depending on the severity, they may recommend physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, or surgery.
If you want to learn more about pinched nerves and neuropathic pain, we have an article here.
When Should I Worry About Upper Back Pain Between Shoulder Blades?
It’s important to note that pain in between your shoulder blades is not exclusive to nerve compression or damage. Other conditions can come with this symptom, so it’s best to be on the lookout for other symptoms that may point to a more serious condition. These include:
- Difficulty in breathing (such as shortness of breath)
- Chest pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Fever
If these symptoms accompany the pain, it may indicate a possible heart attack or lung disease. Do not delay medical attention in these cases.
Similarly, if your pain is the result of a traumatic injury, such as a car accident, it is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Delayed medical treatment increases the risk of long-term complications.
Persistent pain should also be adequately evaluated. Pain that lasts longer than a few weeks and is not relieved by rest or OTC pain drugs may be a sign of a more severe condition. In such cases, medical attention is necessary to determine the underlying cause of the pain. A proper diagnosis is essential in developing an appropriate course of treatment.
Can MRI Show Nerve Damage in the Shoulder?
When diagnosing nerve damage in the shoulder, an MRI can provide valuable information to help diagnose and treat the issue. An MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a medical test that uses magnets and radio waves to create images of the inside of the body. It can provide detailed images of the internal structure of the shoulder.
An MRI can help identify the source of the nerve damage. It can reveal any abnormalities or changes in the shoulder joint structure and surrounding areas. For example, an MRI can show if there is a herniated disc or other structural issues that are compressing the nerve.
In addition to providing information about the structure of the shoulder, an MRI can also assess nerve function. Specialized MRI techniques can be used to evaluate the integrity of the nerves and identify any areas of damage.
An MRI can be a helpful tool in diagnosing nerve damage in the shoulder. However, it is just one component of a comprehensive evaluation. Your healthcare provider will consider other factors when making a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Takeaway
Nerve pain in between your shoulder blades is usually due to nerve compression. A nerve commonly associated with this symptom is the dorsal scapular nerve. Numerous conditions can cause nerve compression. These conditions may require different treatment approaches.
If you're suffering from nerve pain between your shoulder blades, there are a few steps you can take to ease your discomfort. Seeking medical advice from a healthcare professional (like a doctor or physical therapist) should always be the first step in addressing nerve pain.
You may relieve your nerve pain by incorporating certain lifestyle changes into your routine. Gentle exercises, heat therapy, and practicing good posture can help prevent nerve pain from occurring in the first place.